The flocculation of suspensions by chemical flocculants is used to improve solid-liquid separation in mineral processing operations, wastewater treatment, and so on. The currently accepted chemical flocculants are synthesized high-molecular-weight polymers and alum. Unfortunately, both of these flocculants are environmentally undesirable, since chemically synthesized polymer flocculants remain in natural environments for long periods without degradation to less harmful forms.
In recent two decades, many studies concerned environmentally friendly biodegradable flocculants have been reported; naturally existing polymers such as chitin or chitosan, methylated proteins, extracellular polymers produced by bacteria, chemically modified natural polymer or polysaccharide (starch-based flocculant, cellulose-based flocculant, alginate-based flocculant, and so on).
On the other hand, let me tell you something else, fillet of salmon, cod, and so on have been used for food all over the world. In the other hands, however, fish milt of salmon, cod, sandfish and so on, have been used for food from old times in Japan only, and most salmon milt has been discarded because of an inherent fishy smell, a fast decline of freshness, and difficulty for food processing due to lacking heat coagulation. In the world, a huge amount of fish milt has been discarded. Salmon milts include a lot of protamine as a nucleoprotein, which has a basic group, such as amino or guanidine functional group, and has a positive charge in the neutral pH region.
A surface charge of solid particles in the aqueous phase is known as a negative charge mostly. These suggest that protamine can adsorb onto suspended particles surface and can become a flocculant for suspended solid particles.
However, judging from the molecular weight of protamine (Mw. ca. 4600), the molecular size of protamine should be relatively small than other proteins used as flocculants. Novel flocculants are needed to have a certain size for making effective flocs in the flocculation process.
Bridging flocculation could occur under the situation which flocculant size is larger than the closest possible distance between surfaces of adjacent solid particles. The distance would exist because of electrostatic repulsive force between surfaces which were same charge. It has been pointed out that one of the conditions for having an excellent flocculant is that it is important to have a size exceeding this distance.
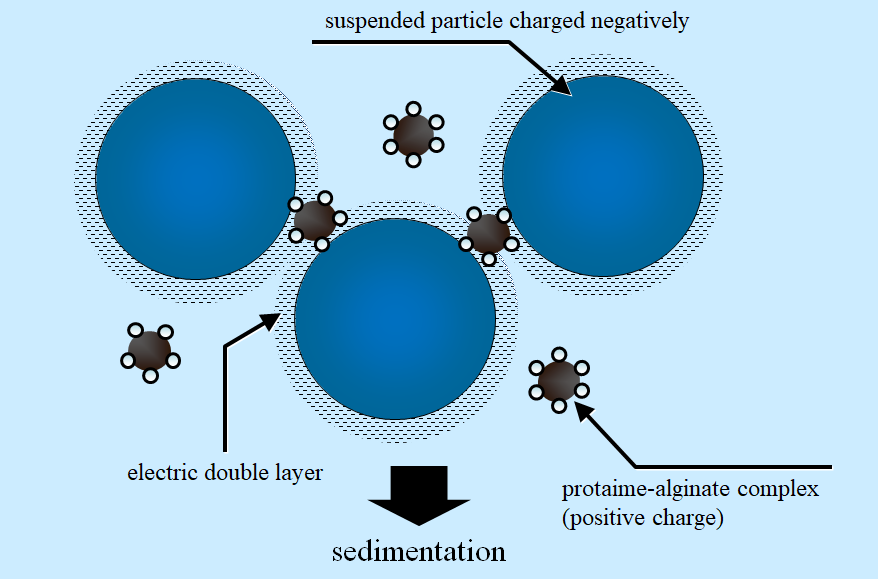
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of electric double layer existing at surface of suspended particle in aqueous environment and the proposed protamine-alginate complex flocculant.(Reference: Kashiki and Suzuki, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 25, 444 (1986))
As described above, polysaccharides have been employed as bio-flocculants. Major polysaccharides used as bio-flocculant were mainly alginate, chitosan, cellulose, starch, pullulan, xanthan and pectin and so on. Among these, one of the polysaccharides, alginate is a major structural polysaccharide from brown seaweeds, Brown algae are very familiar to us because they are widely distribute along the coast of Japan. In addition there are many unlitilied and unedible species of brown algae.
Alginic acid, a linear polysaccharide of beta-D-mannuronic acid and alpha-L-guluronic acid, is a main cell-boundary constituent of brown algae. Alginic acid contains about 4x103 mol/g of carboxylic groups. By these ways, cationic properties were added to alginate polymer to bind with solid surfaces charged negatively in aqueous environment.
We proposed the utilization of a complex of two substances, alginate polymer and protamine as an environmentally preferable flocculant in the aqueous phase, and examine the expression of flocculation ability and the capabilities of the alginate-protamine complex to flocculation of suspended solid particles. By this method, relative larger size and charged positively polymer as a flocculant could be obtained without some complicated chemical modifications.
Kaolin and quartz were chosen model solid particles. We investigated especially the expression of flocculation ability of the complex, the influence of the mass ratio of alginate and protamine and pH value of the suspension on the flocculation in the present study.