The flocculation efficiency was evaluated with the relative absorbance, A/A0, where A and A0 represent the absorbance of the suspensions in the presence and the absence of flocculant, respectively.
Typical results are shown in figures 2 and 3.
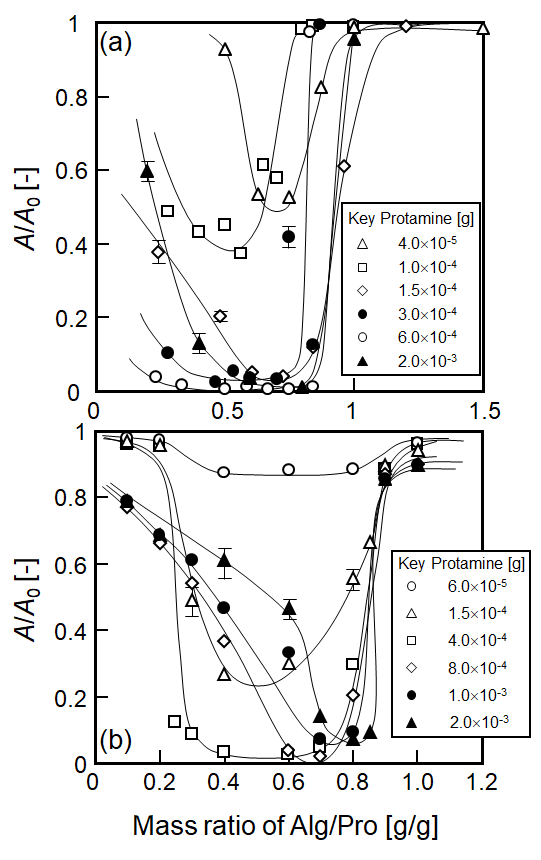
Figure 2 Influence of mass ratio of sodium alginate (Alg) and protamine (Pro) on the relative absorbance, A/A0, for (a) kaolin and (b) quartz particles. Each symbol corresponds to protamine content of the mixture.
Influence of the mass ratio of aliginate and protamine on the flocculation efficiency is shown in Figure 2 for kaolin (Fig. 2a) and quartz (Fig. 2b), respectively. The experiments were conducted at pH 6.9-7.0. For both kaolin and quartz, the degree of clarification was higher in the range of mass ratio ca. 0.3-0.8. Especially, in cases of 4.0x10-4 and 6.0x10-4 g for protamine content in the mixture for quartz and kaolin, the most effective clarification was observed in the experimental range of this study.
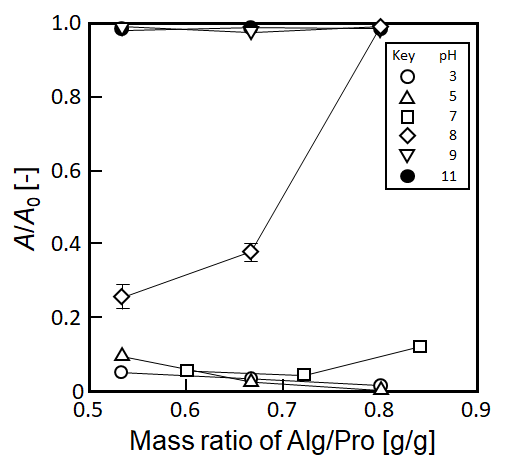
Figure 3 Influence of pH value of the kaolin suspension and mass ratio of sodium alginate (Alg) and protamine (Pro) in the mixture on the relative absorbance, A/A0, of kaolin suspension. The content of protamine is 1.5x10-4 g.
Influence of the pH value on the flocculation efficiency is shown in Figure 3. kaolin particle was employed as a model solid particle and the pH value of the 3 g/L suspension was varied by addition of HCl or NaOH solutions. The content of protamine in the mixture solution was fixed at 1.5x10-4 g and that of alginate was varied. At pH 3, 5 and 7, A/A0 value mostly became under ca. 0.1, thus, good clarification by flocculation was observed. On the other hand, at pH 9 and 11, flocculation obviously did not occur in the system. At pH 8, flocculation ability became getting worse with an increase in the mass ratio of alginate and protamine in the mixture solution. The reason why the complex flocculant has the flocculation efficiency in pH 7 was described in the section 3.3. On the other hand, in the alkaline pH region (pH 8-11), especially, a hydrogen ion dissociated from the guanidine and the amino groups, which resulting the both functional groups became uncharged state. This should be considered that the complex as the flocculant could dissociate into protamine and alginate and the flocculation performance disappeared.