Radiocarbon Isotope Dating Method
Section outline
-
-
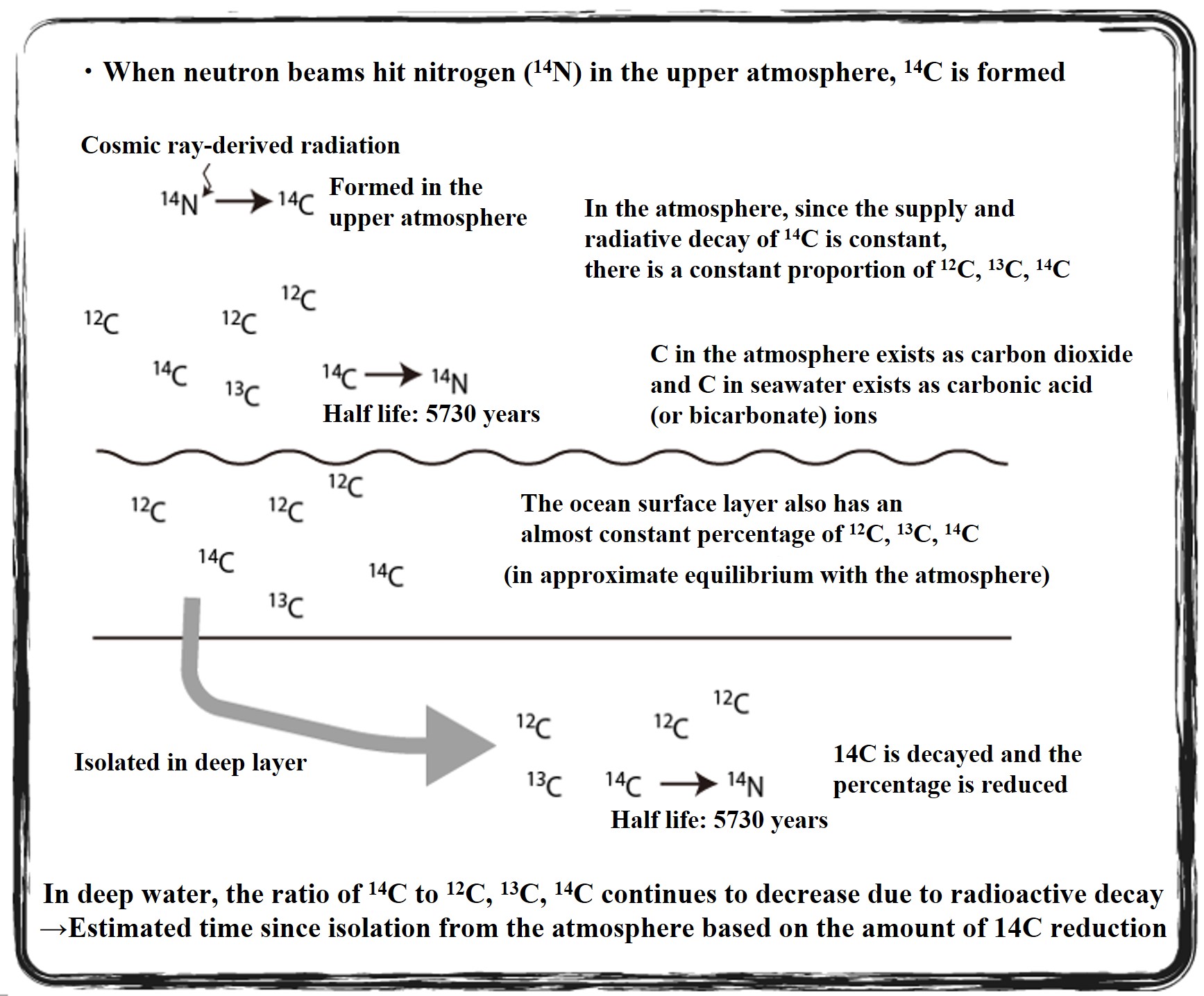
Radiocarbon isotopes (14C) are produced in the upper atmosphere and disappear at a constant rate due to radioactive decay. Since the ratio of the rate of supply to disappearance is nearly constant, the 14C/13C/12C ratio of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and in the ocean surface layer in equilibrium with the atmosphere has been nearly constant from the past to the present. When the 14C supply from the atmosphere is cut off, the 14C ratio decreases at a constant rate. The 14C dating method estimates the number of years since the 14C supply from the atmosphere was cut off by examining the 14C ratio of carbon in an environmental sample. This is used to trace the deep circulation of the oceans.
-
(To learn more about radionuclides produced by cosmic rays, go to this link)
-
High-energy cosmic rays are emitted from supernova explosions and other events in the universe. When these cosmic rays hit air molecules in the upper atmosphere, the atomic nucleus is broken and neutrons are ejected. When the neutron strikes a nitrogen atom and is replaced by a proton in the nucleus, it becomes 14C. The neutrons in radioactive 14C eventually β-decay (eject electrons) to protons, which return to 14N. If production and annihilation are constant, the amount of 14C in the atmosphere will remain constant. Based on the ratio of stable carbon (12C) to 14C, 14C dating estimates the number of years since the 14C supply from the atmosphere was cut off.
Let's understand its simple calculation.
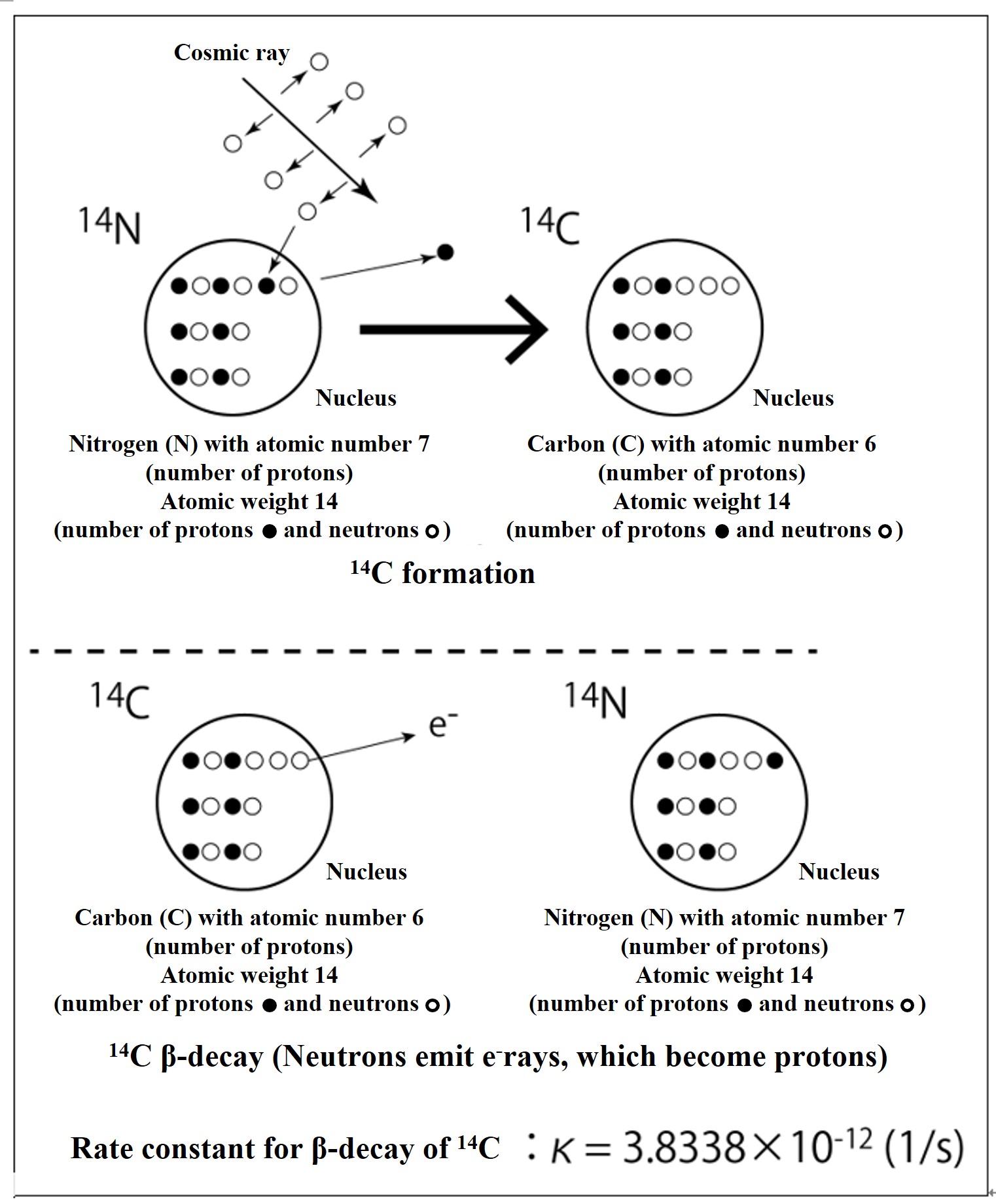
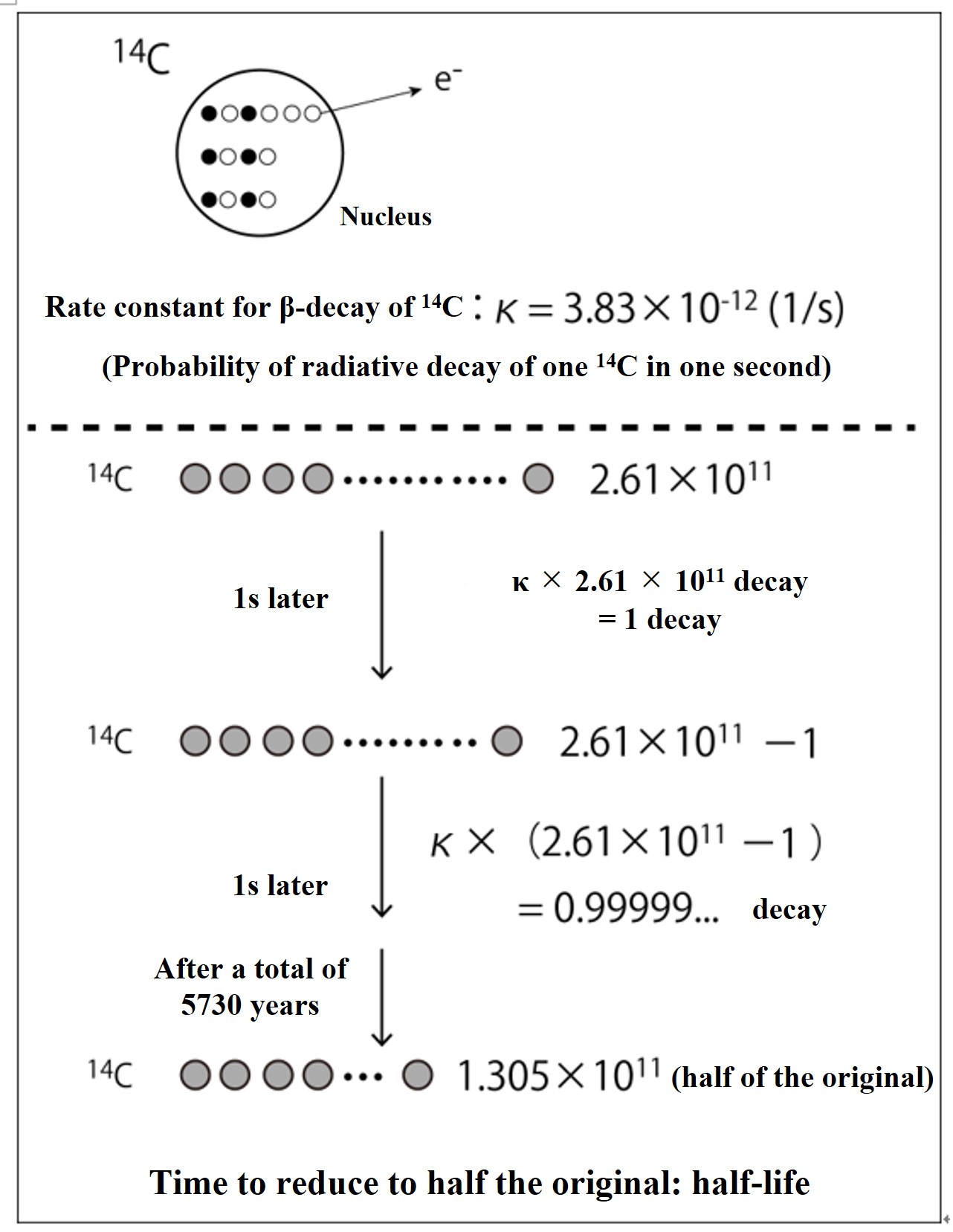

I have added explanations to help you understand the concepts of the 14C dating method and to enable you to perform simple calculations. The half-life estimates used for 14C dating require complex calculations based on radiation science, but we have omitted those details. Consider it an overview.
-
Based on the ratio of 14C and 12C present in an environmental sample, we calculate the number of years since the sample was cut off from the 14C supply from the atmosphere.
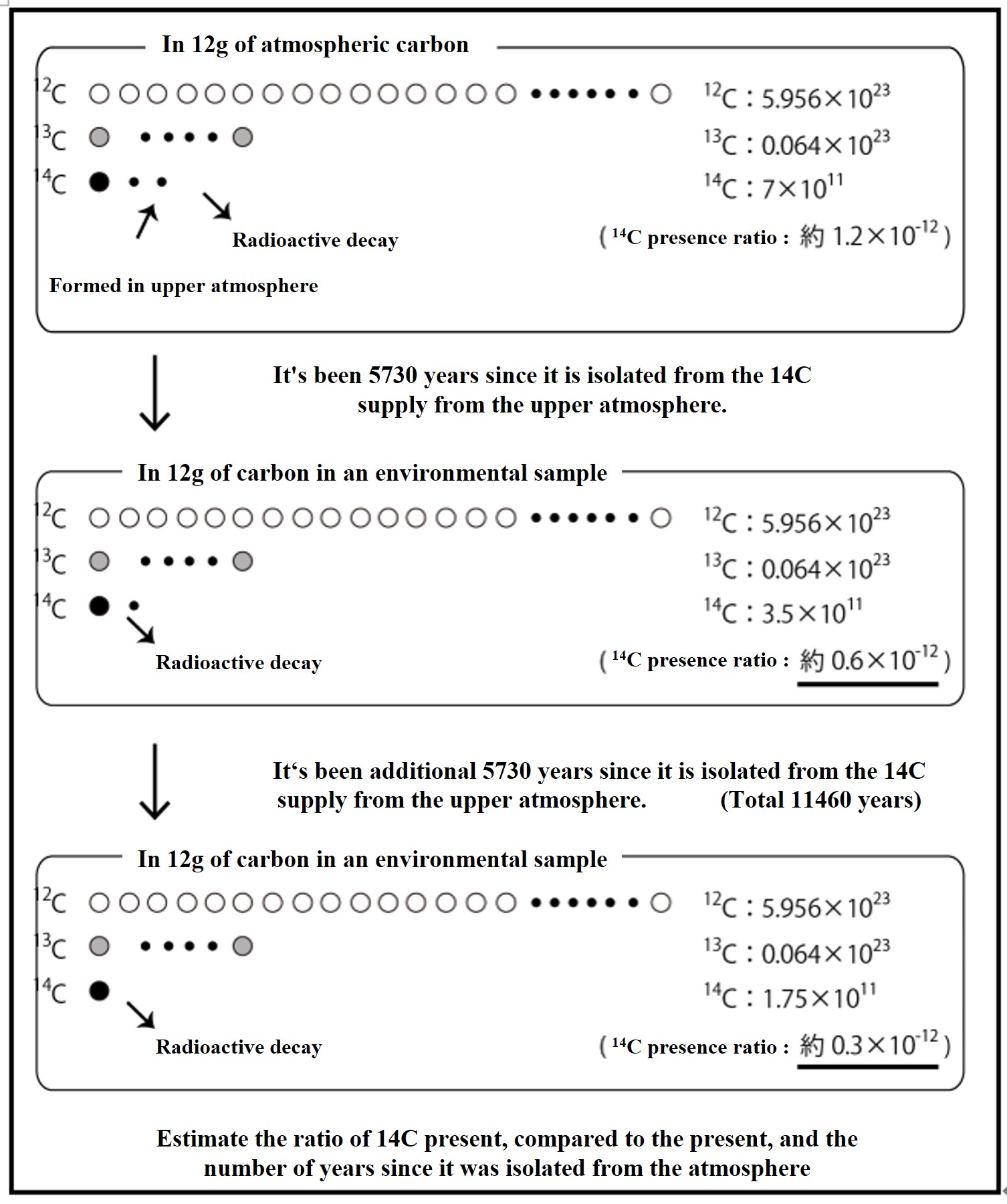
-
How much radioactive decay is occurring in your room and body every second? Here is an example of a simple calculation.
-

