Material Cycle Studies in the Polar Ocean
Section outline
-
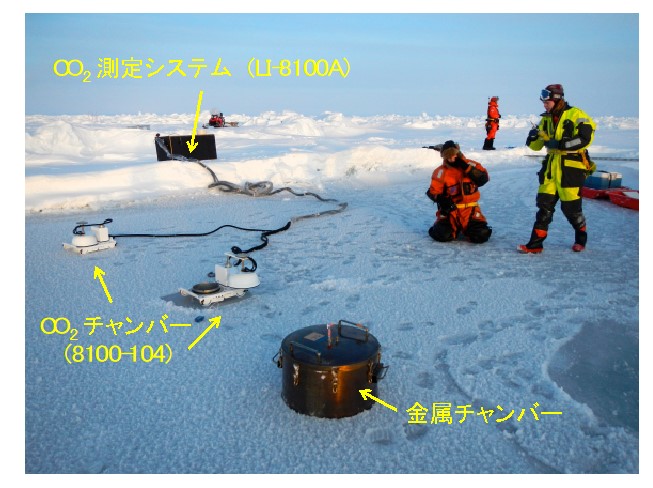
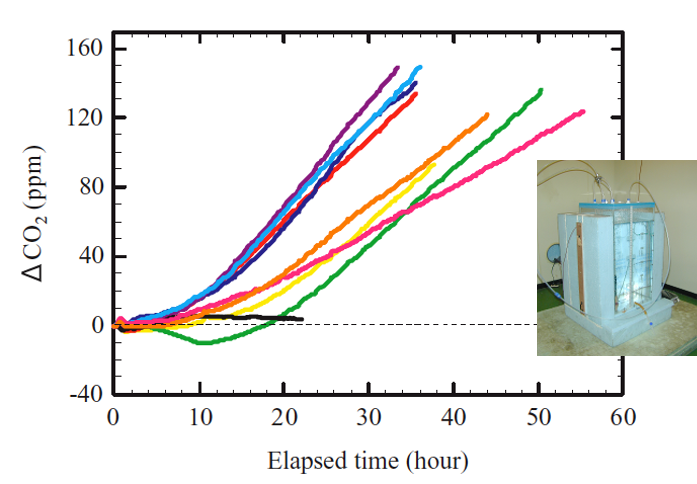
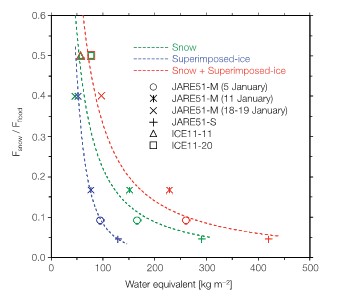
In very cold places, vast of ocean freezes like puddles on the road side and ponds freeze in winter. The ocean is covered with ice, the whole area becomes pure white, and the fantastic world expands. The presence of ice is deeply involved in climate change as it affects global heat and the transport of substances. Our research group conducts field observations on frozen oceans such as the Antarctic, Arctic, and Sea of Okhotsk.We conduct research, focusing on the absorption and release of greenhouse gasses such as carbon dioxide by the frozen ocean and the material cycle of nutrients and carbon.