【Plankton net】
Plankton nets are made of nylon mesh (Fig.
2) sewn together into a cone, cylindrical cone, or square cone shape, with the
opening (mesh mouth) fixed to a metal frame. By moving the net in the water,
plankton is filtered out of the seawater.
The most typical and simple structure of a
plankton net is shown in Fig. 4-a. Three bridle ropes and three manropes are
connected to the top and bottom of the net mouth ring, respectively. The
bridle rope is connected to the winch wire rope via a retractable fitting called
“swivel”. A weight is suspended from the manropes to keep the net submerged in
the sea. At the tail of the net, there is a cod-end that collects the sample,
which is opened to remove the sample. By attaching a flow meter to the net
mouth, the amount of seawater that has passed through the net mouth (filtration
volume) can be estimated.
To facilitate comparisons between samples
collected in different areas and at different times, Dr. MOTODA Shigeru
(Professor Emeritus, Hokkaido University) devised the North Pacific Standard Net
(NORPAC net), which has a net mouth ring with 45 cm diameter and a 180 cm
filtration side length (length of the net). It was also decided that the
vertical towing method should be used to haul the net from a depth of 150 m at
a rate of 1 m per second. The "twin NORPAC net" (Fig. 4-b), which
consists of two NORPAC nets connected together, allows plankton nets with
different mesh sizes to be attached to each ring, so that samples with
different properties can be obtained simultaneously in a single tow.
Link to observation method “Collection of planktonic organisms by plankton net”
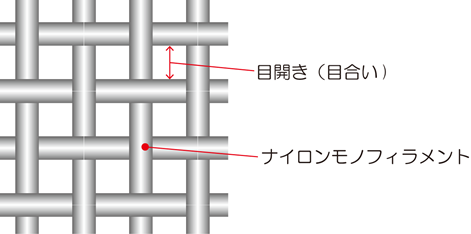
Fig. 2 Enlarged view of nylon mesh
目開き(目合い): mesh size of net
ナイロンモノフィラメント: nylon monofilament
Nylon mesh is available in various standards
depending on the thickness of the yarn (nylon monofilament), its weaving
method, and the size of the mesh size. Nylon mesh is also widely used for
sifting products in flour mills and for filtering out impurities in industrial
products.
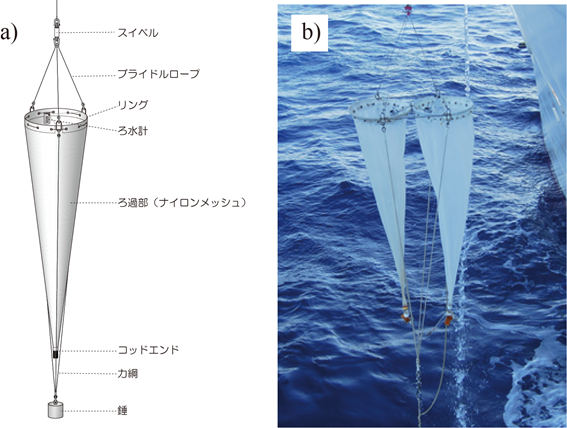
Fig. 3 NORPAC net: North Pacific Standard net
a) Composition of “NORPAC net” b) “twin NORPAC net”
スイベル: swivel ブライドルロープ: bridle rope リング: net mouth ring ろ水計: flow meter
ろ過部(ナイロンメッシュ): filtration section (nylon mesh)
コッドエンド: cod-end 力綱: manrope 錘: weight



