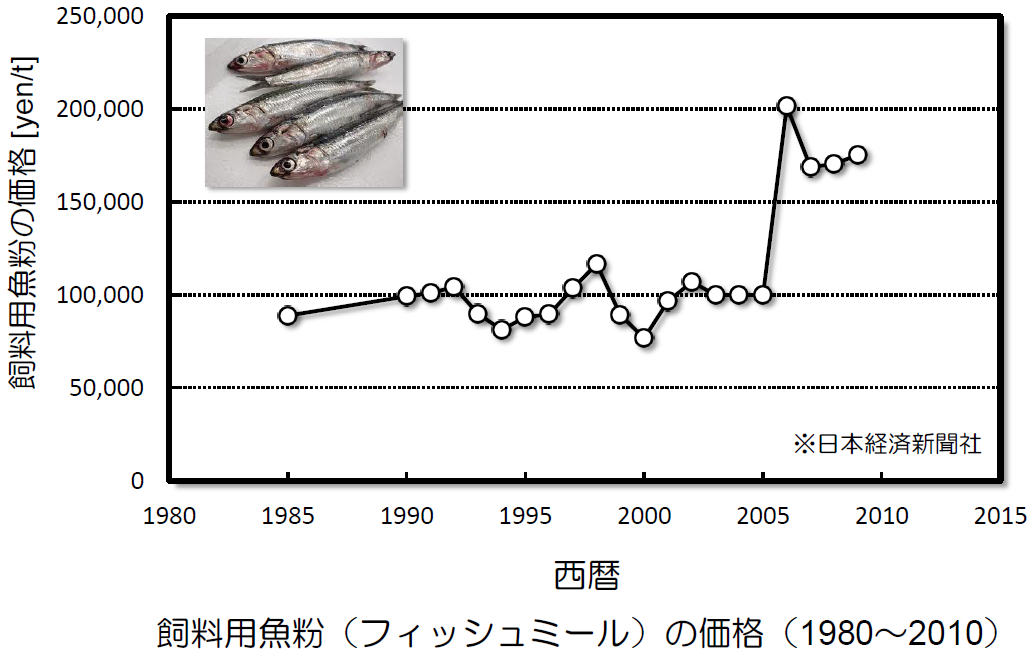
Price of fishmeal for feed (1980~2010)
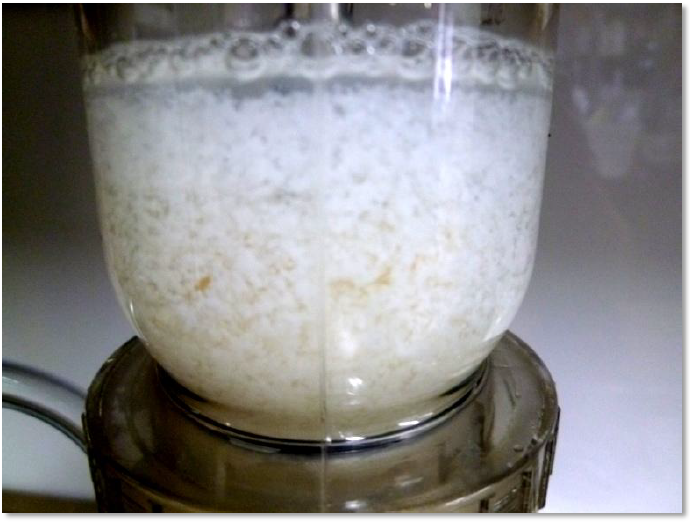
The price of fishmeal, which is the main ingredient of aquaculture feed, is soaring. We believe that if wastewater from food processing plants is treated with a safe protein-derived coagulant, the recovered SS can be used as a substitute for fishmeal.
Coagulation treatment of wastewater from wheat gluten manufacturing plant
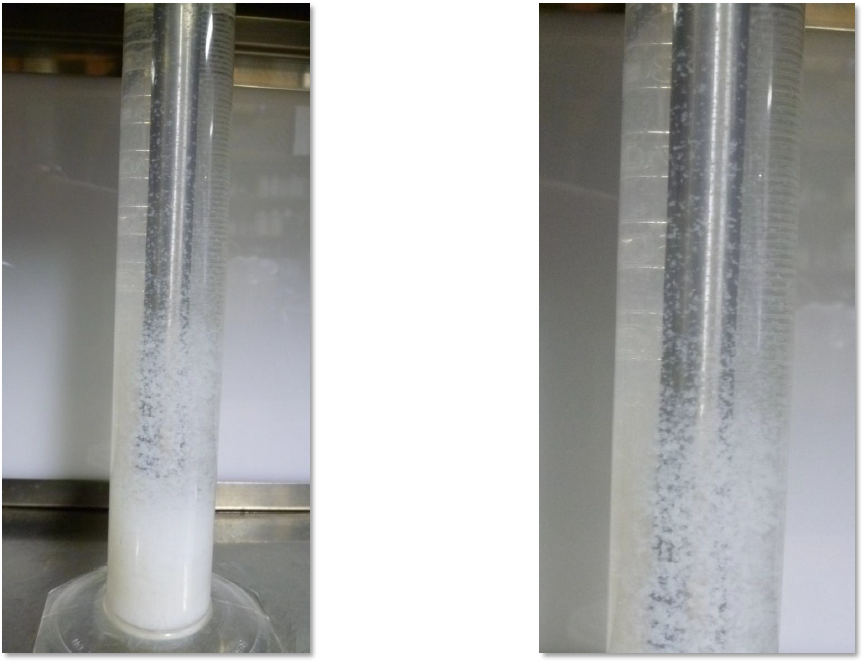
Agglomeration treatment of wastewater from tofu manufacturing plants
