H2 and O2 exist in the original form of the reaction system, and H2O exists in the product form (see the figure below). The binding energy change of the reaction system including the generated form and original form is T・⊿S【generated form】―【original form】(in the figure below, it is shown as T・⊿S system). When this reaction occurs, the heat of reaction (⊿Q) is transferred to the outside world. Considering the outside world, the outside world receives heat ⊿Q, so the entropy of the outside world increases by ⊿Q/T. However, the outside world is sufficiently large, and the temperature T, including the outside world, remains the same before and after the reaction.
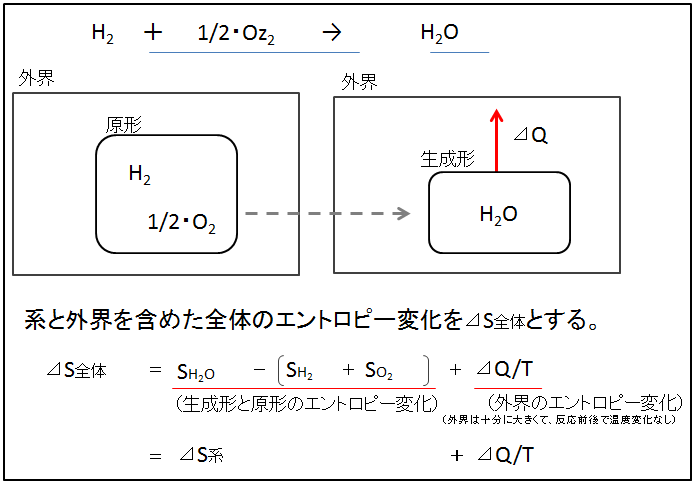
外界outside world 系と外界を含めた全体のエントロピー変化を⊿S全体とするLet the entropy change of the whole including the system and the outside world be ⊿Sentire 生成系と原形のエントロピー変化Entropy change of generation system and original form 外界のエントロピー変化Entropy change in the external world 外界は十分に大きくて、反応前後で温度変化なしThe outside world is large enough that there is no temperature change before and after the reaction.
If the overall entropy change including the reaction system and the outside world is ⊿Sentire, then
⊿Sentire = ⊿S【generated form】-【original form】 + ⊿Q/T
holds true. Since this system including the outside world is sufficiently large and there is no temperature change, it can be considered an adiabatic system. In other words, in this system, the entropy increases (
Sentire > 0).
If we impose the condition of increasing entropy,
⊿Sentire = ⊿S【generated form】-【original form】 + ⊿Q/T> 0 ①
Substitute the following formula obtained earlier into this.
⊿H【generated form】-【original form】=T⊿S【generated form】-【original form】+ ⊿G【generated form】-【original form】
→ T⊿S【generated form】-【original form】=⊿H【generated form】-【original form】- ⊿G【generated form】-【original form】
→ ⊿S【generated form】-【original form】=⊿H【generated form】-【original form】/T- ⊿G【generated form】-【original form】/T
Assign to ⊿S in ①
⊿H【generated form】-【original form】/T
- ⊿G【generated form】-【original form】/T +⊿Q/T > 0 ②
Since the enthalpy change and the reaction heat (-⊿Q) are equal (⊿H【generated form】-【original form】=-⊿Q) and T>0,
(The minus sign of -⊿Q is because heat is lost from the system's perspective.)
② is ⊿H【generated form】-【original form】/T
- ⊿G【generated form】-【original form】/T -⊿H【generated form】-【original form】/T > 0
-⊿G【generated form】-【original form】> 0
So
The reaction progresses in the direction of ⊿G【generated form】-【original form】< 0
A chemical reaction is in equilibrium when the entropy of the reaction system and the outside world does not change. In other words, the following conditions hold.
⊿G【generated form】-【original form】= 0
In the next course, we will combine this conditional expression with the thermodynamic function to derive the chemical equilibrium conditional expression that we covered earlier.