Equation of motion of a particle in a fluid (inertia force = gravity - buoyancy force - resistance force)
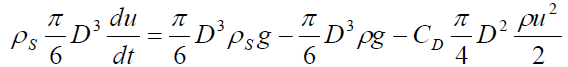 (2-1)
(2-1)
CD coefficient of resistance of a fluid,D Particle diameter,t time,u particle settling velocity,ρ Fluid density,ρs Particle density
When fine particles are dropped into a fluid, they initially undergo an accelerated motion, which soon becomes a constant velocity motion (du/dt = 0). This is called the terminal velocity.
ut = ( ρs– ρ)gD²/18μ (2-2)
ut (m/s) terminal velocity,μ (Pa·s) Viscosity of fluid
The terminal velocity of particles is proportional to the density difference between the fluid and the particles, and proportional to the square of the particle diameter.