Oxygen respiration
Eukaryotes use oxygen to oxidize organic matter to obtain energy (oxygen respiration). In the column below, we have assumed the simplest organic substance, formaldehyde, and described the reaction of oxidation of organic matter by respiration. Under each substance, we note the standard Gibbs energy of formation for each substance. The total energy of the chemical reaction in its product form (right side) minus the total energy in its original form (left side) (⊿∑Gf0) is the energy that the organism can obtain. The reason for the negative energy difference is that, from the reaction system's point of view, the energy is lost and the organism can obtain it.
*Before the reaction is called the original form, and after the reaction is called the product form.
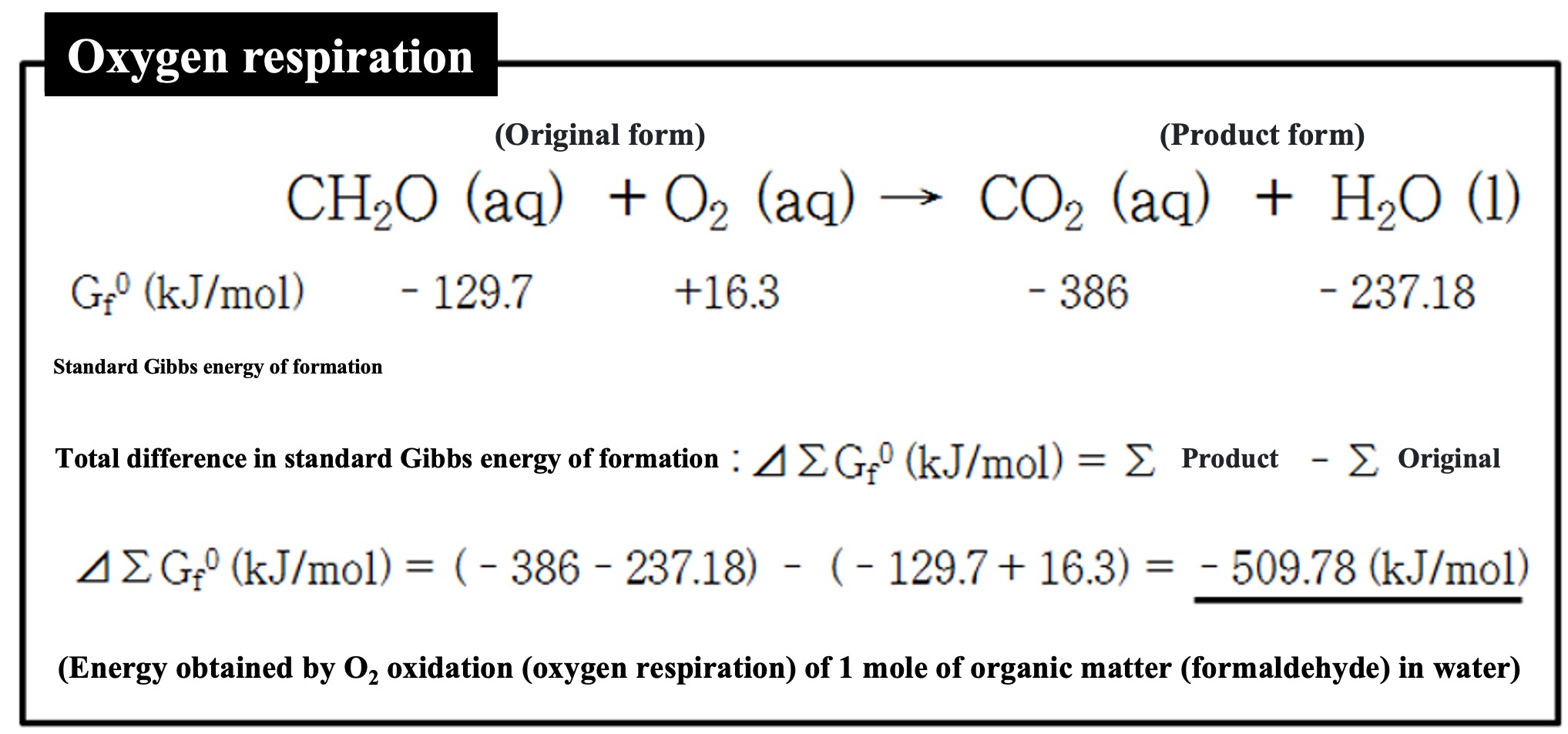
As in this example, the standard Gibbs energy of formation for each substance is written below the reaction equation, and the total difference (⊿∑Gf0) is calculated before and after the reaction (left side: original form, right side: product form). The standard Gibbs energy of formation (Gf0) for each substance is an important thermodynamic constant. It can be downloaded in one previous course.
*The standard Gibbs energy of formation for O2 in its standard state is 0 (kJ/mol), but dissolving it in water produces energy (16.3 kJ/mol). Assuming respiration in water, we used the standard Gibbs energy of formation for O2(aq) as shown above. Also, if the organism exhales CO2 in water, CO2(aq) should be used, but if it exhales into the gas phase, the CO2(gas) value should be used. Even when plants in water use CO2 in photosynthesis, or whether it is H2CO3 or HCO3-, the energy used in the calculation will change. In this course, I have dealt with that in an appropriate manner.