Hundreds of millions of years since the ocean was formed
There is a limit to the amount of carbonate particles that can be retained at the ocean floor. Once the ocean floor is covered with carbonate rocks, it will be difficult for Ca2+ to leach out of basalt, and if the ocean floor moves and burrows into the Earth's interior, carbon dioxide will return to the atmosphere as volcanic gases. Nevertheless, by 3 billion years ago, the atmospheric partial pressure of carbon dioxide had dropped to 20 (atm).
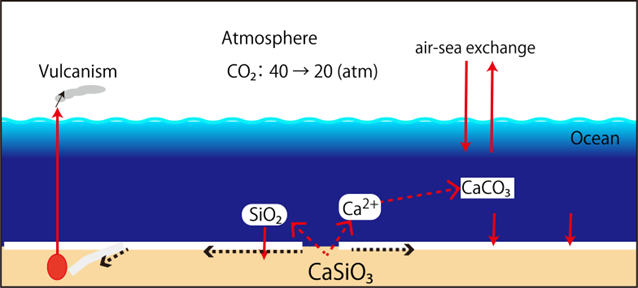
The figure above shows an image of an ocean ridge and subduction into the mantle. This can lead to continental growth. Here, assuming that the continents have grown rapidly since 3 billion years ago, we assume that atmospheric carbon dioxide has been reduced by half just before that time (Reference: TAJIKA Eiichi, The 4.6 Billion Year History of Earth's Environmental Changes).

