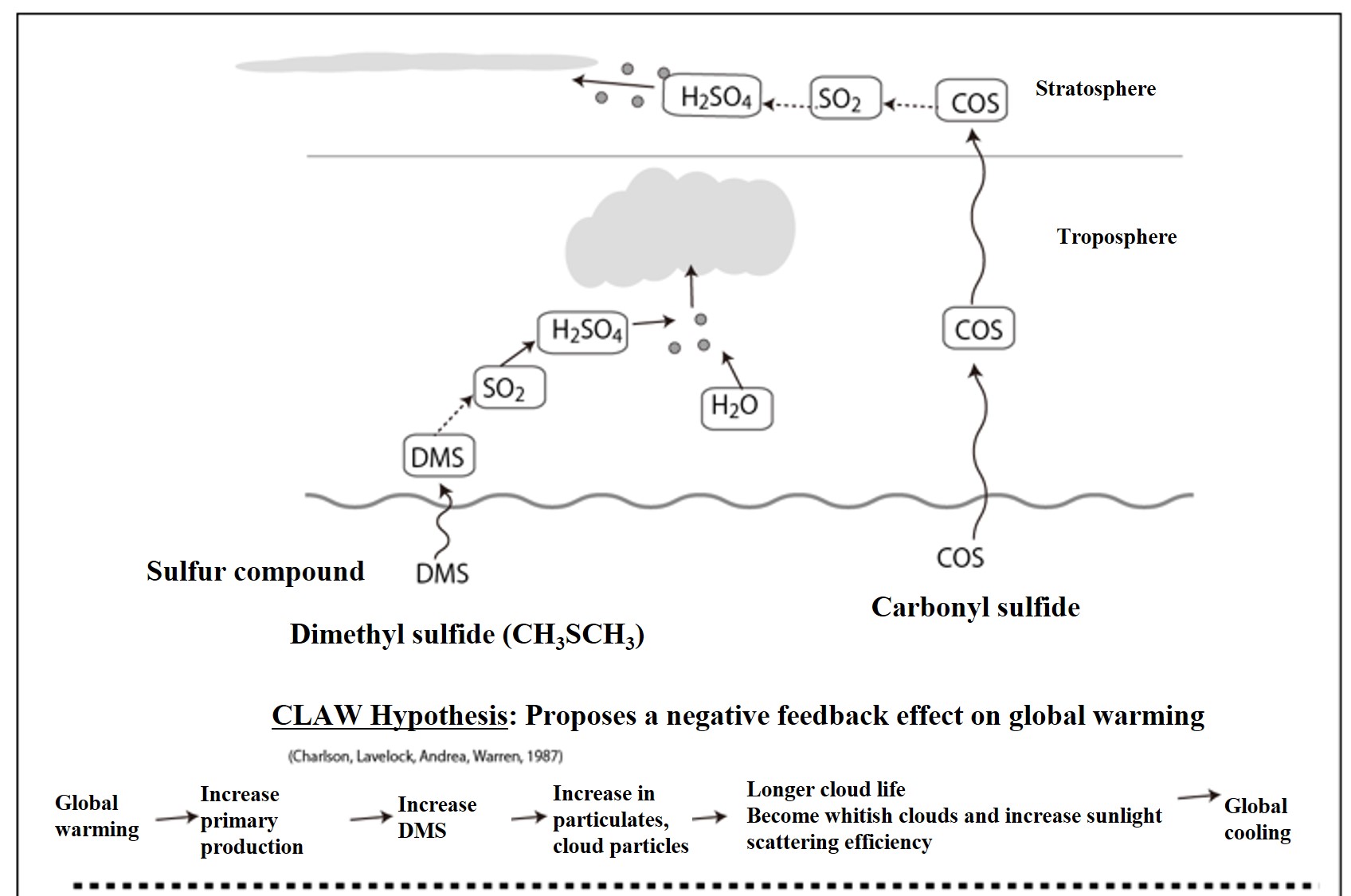
CLAW hypothesis
DMS is a relatively reactive organic sulfur gas that undergoes an oxidation reaction to sulfur dioxide (SO2) in a short time (about several days) when released into the atmosphere. SO2 in the atmosphere is further oxidized to sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which reacts with water, ammonia, and sodium chloride to form fine particles of ammonium sulfate and sodium sulfate. The sulfate particulates can become nuclei (seeds) of cloud grains through repeated coagulation and growth. The relationship between oceans, weather, and climate is attracting attention because DMS released from marine plants can become cloud seeds.
There are many other components that can be the seeds of cloud particles, including sea salt particles, anthropogenic sulfate particles, nitrate, and many others. When limited to oceanic atmospheric clouds, sulfate particulates derived from DMS released from marine plants are considered to be the most important. DMS-derived cloud particles can also have a significant impact on climate. The CLAW hypothesis was proposed, which states that if the Earth warms, DMS will increase and function to mitigate warming.
In other words,
① As the Earth warms,② photosynthesis by marine plants becomes more active.
③ More marine plants increase DMS production by marine plants, which increases DMS release into the atmosphere.
④ As DMS release into the atmosphere increases, the amount of DMS-derived sulfur dioxide and sulfate particulates increases.
⑤ As the number of DMS-derived sulfate particles increases, the number of particle nuclei (cloud nuclei) that grow into cloud grains increases.
⑥ As the number of cloud nuclei increases, the size of each cloud particle decreases.
⑦ As the size of each cloud particle decreases, the rate at which clouds reflect sunlight (albedo) increases. The frequency of rainfall as rain decreases, so cloud dwell time increases.
⑧ The increase in cloud albedo and the increase in cloud dwell time will create a cooling effect near the earth's surface.
In other words, the effect of ① (global warming) → ⑧ (cooling) is generated. This is called the negative feedback effect on global warming, and the CLAW hypothesis proposes that the earth itself has the ability to mitigate the climate through the series of events ①→②→・・→⑧.
Since the CLAW hypothesis was proposed in 1987, climatologists, oceanographers, and atmospheric scientists around the world have been absorbed in research to test the CLAW hypothesis. This has led to major advances in atmospheric and oceanographic science. On the following pages are the papers in which the CLAW hypothesis was disproved.

