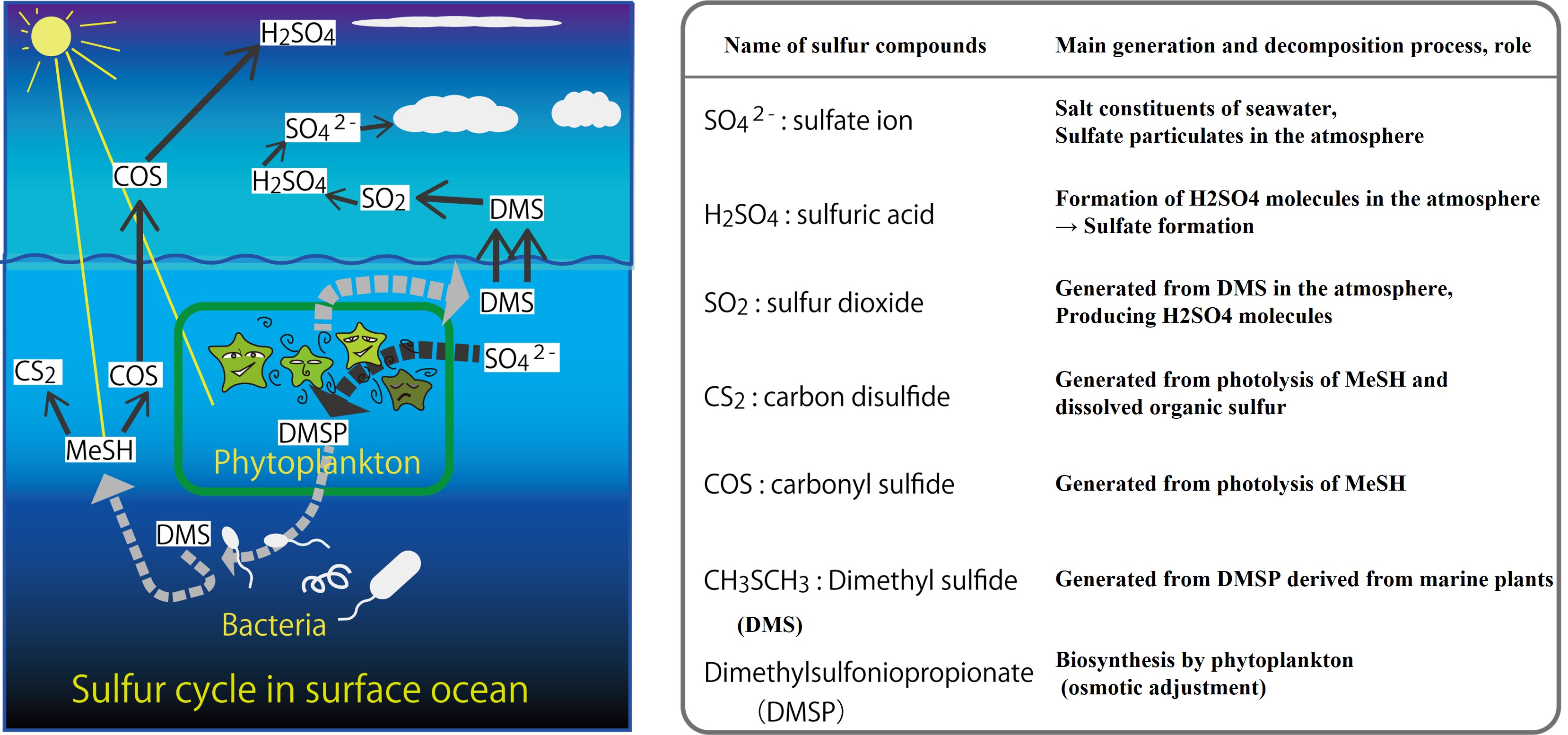
Organic sulfur gases -Sulfur cycle in the ocean and atmosphere-
This image depicts the sulfur cycle in the ocean surface layer and the atmosphere. The oceanic sulfur cycle is driven by the activities of marine phytoplankton and bacteria. Organic sulfur gases, when released into the atmosphere, become a source of sulfuric acid particulates. It plays an important role in the atmospheric environment.
【In the sea water】
- Marine plants use SO42- ions in seawater to biosynthesize Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP), which is used for osmotic adjustment.
- When DMSP is decomposed in plant cells or by bacterial action in seawater after the cells have died, it becomes CH3SCH3 (dimethyl sulfide; DMS).
- In seawater, DMS is converted to methanethiol (MeSH) by bacterial action.
- MeSH photolyzes in seawater to COS and CS2.
【In the atmosphere】
- When DMS is released into the atmosphere, it is oxidized to sulfur dioxide (SO2) and then to sulfuric acid molecules.
- When COS is released into the atmosphere, it reaches the stratosphere where it becomes SO2 and then sulfuric acid molecules.
- Sulfuric acid molecules in the atmosphere condense with surrounding water molecules and ammonia molecules to form fine particles that become the source of cloud particles.
Dimethyl sulfide (DMS; CH3SCH3) is the most abundant organic gas in seawater, accounting for more than 90% of all organic gases. Since it is derived from marine plants, high concentrations of DMS are often observed in areas of high biological productivity. The seawater concentration of methanethiol is about 1/10 to 1/100 of DMS.
Extra (Future Prospects) The organic matter with a thiol group (-SH), including methanethiol, may occupy an important position as a reducing substance in seawater. In the ocean, reducing organic sulfur compounds may be responsible for changes in the chemical forms of trace elements (iodine or iron, for example). Traditionally, the oceanic sulfur cycle has only focused on the ability of DMS to form cloud grains, inspired by the CLAW hypothesis. In the near future, I believe that research on the relationship between the sulfur cycle and trace element dynamics driven by the action of marine microorganisms and the redox state of the oceans will be the focus of attention. This is going to be a major undertaking, and I would like to see an all-Japan system of oceanography. Currently 1 member! Now recruiting members.

