Solve practice problems using the basic equations of chemical equilibrium.
Exercises) Find the equilibrium concentration of sodium chloride in solution using the thermodynamic constant.(Not a redox reaction)
【Procedure】
① Describe the reaction equation for the dissolution equilibrium.
② Standard generation Gibbs energies are noted below each substance.(Please read from the list)
③ Calculate :【Total energy of the generated form】-【Total energy of original form】
Multiply by 1000 to remove the kilo (k).
④ Substitute into equilibrium condition equation(energy difference= -RTLn K)
⑤ K=(Concentration product of product form)/(Concentration product of the original form)
However, the concentration of the solid in the solution reaction is assumed to be 1.The concentration of a saturated solution of sodium chloride is determined, so the NaCl crystals (solids) remain dissolved. [NaCl] = 1
⑥ When NaCl dissolves, only the same amount of Na+ and Cl- is produced, so [Na+] = [Cl-].
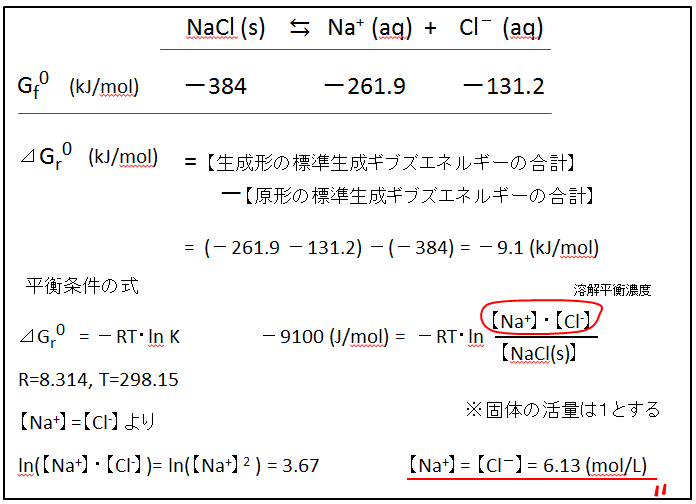
正成形の標準生成ギブズエネルギーの合計:Total Standard Generated Gibbs Energy of Positive Formation
原形の標準生成ギブズエネルギーの合計:Total standard generated Gibbs energy of original form
平衡条件の式:Equilibrium condition equation
溶解平衡濃度:Dissolution Equilibrium Concentration
固体の活量は1とする:The activity of a solid is assumed to be 1
*Note that in Gibbs energy units, kJ/mol is followed by kilo (k).
It is easy to experimentally determine the equilibrium concentration of sodium chloride in solution. A saturated solution is one in which sodium chloride crystals are well mixed in water, and the crystals remain dissolved after standing overnight. The saturated concentration can be obtained by taking a certain amount of the saturated solution, evaporating it to dryness, and measuring the weight of the residue. However, since saturated solutions have high ionic strength, the activity coefficient must be taken into account.