Blank measurement
A sample that does not contain the target component is called a “blank sample”. As I have mentioned many times, in environmental analytical chemistry, blank measurement is extremely important to ensure the quality of analysis results. A blank sample is always measured when dealing with various problems in analytical chemistry, such as how low concentrations can be quantified and whether there is any effect of contamination of the target component.
Instrument blanks and operational blanks
An instrument blank is a measurement performed by introducing an ideal blank sample into the sample inlet of the analyzer, or measuring without introducing any sample. Here, the ideal blank sample is ultrapure water for water analysis or ultrapure nitrogen for gas analysis. Instrument blank results are used when demonstrating the performance of the instrument itself.
Apart from this, in environmental analytical chemistry it is extremely important to examine the operating blank.An operation blank is a blank measurement when all these operations are performed on a blank sample, from sample collection to storage, sample pretreatment, and introduction to the analyzer.
Why is that necessary? As mentioned at the beginning of this course, in environmental analytical chemistry, samples are collected from all over the world, brought back to the laboratory, and finally analyzed. It can also detect picograms, femtograms, and ultra-trace components in environmental samples. Any operation can lead to sample contamination or loss, and the unpredictable. Operational blanks should be examined to ensure the validity of analytical results for environmental samples.
Examples of equipment selection and operation blanks when investigating components contained in rainwater
【Equipment selection】
First and foremost is the material of storage containers and laboratory equipment. It is necessary to choose the material according to what is to be measured. For example, when measuring ionic components in rainwater, plastic containers made of polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), polyethylene (PE), and polyvinyl fluoride (Teflon, etc.) should be used.
What about glass products, You thinkGlass made of sodium borosilicate releases sodium ions, so it is not suitable for long-term storage bottles.
What is the best material for examining organic matter in rainwater? Since plastic is a carbon product, carbon contamination is possible. Glassware would be nice. Quartz fiber filters should also be used to filter rainwater if trace levels of dissolved organic carbon are to be measured. Before using the quartz filter, it is necessary to heat it at 500°C for about 30 minutes to remove the attached organic matter.
What if you want to study soot particles in rainwater? Plastic products tend to stick soot particles to their surfaces, making it difficult to collect all of them. Glassware may be better in this case.
You should also pay attention to how you store it. Freezing seems to keep the ingredients intact.However, if it is a gas component, it may be removed during freezing. Refrigeration may allow bacteria to grow in the sample water. A saturated solution of mercuric chloride is sometimes added to 1/1000 of the volume of the sample water to stop biological activity. What should I do with the bottle cap? If you want to measure the gas components, it is better to use a butyl rubber plug and an aluminum seal.
In this way, just choosing the material requires various know-how, ingenuity, and attention. With these precautions taken into account, blank measurements are essential to prove that there are no problems with the analysis.
【operation blank】
A blank measurement is performed in a form that reproduces the actual rainwater collection as much as possible.
for example,
① It may be necessary to expose the rainwater collection funnel to the atmosphere for a period of time to check for contamination (complete deposition) when it is not raining.
② Assuming rain, it is better to pour ultrapure water on the funnel and collect, store, and analyze the water in the same procedure as the actual observation.
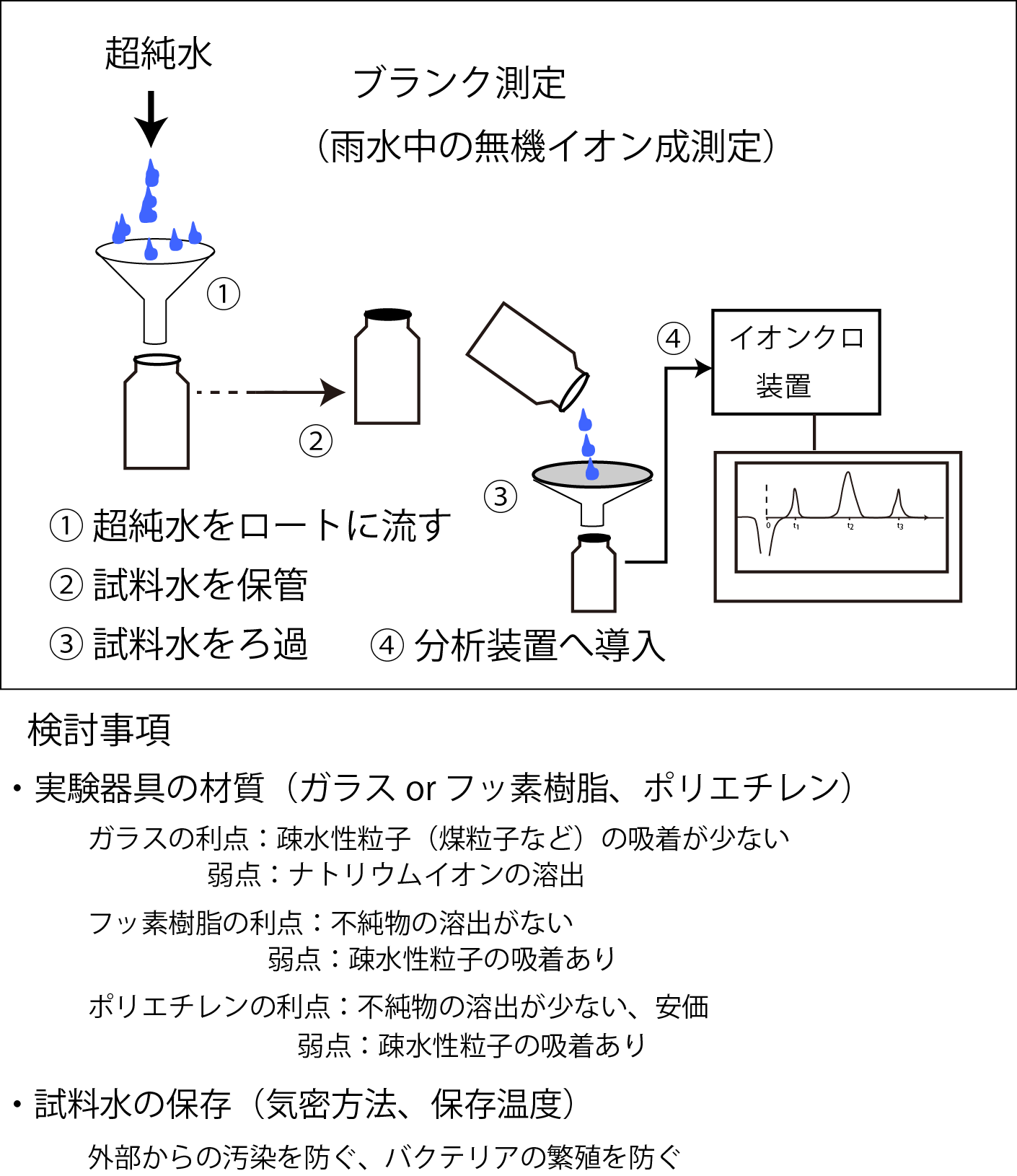
超純水ultrapure water ブランク測定Blank measurement 雨水中の無機イオン成分測定Measurement of inorganic ion components in rainwater イオンクロ装置ion chromatography device 超純水をロートに流すPour ultrapure water into the funnel 試料水を保管Store sample water 試料水をろ過Filter sample water 分析装置へ導入Introduction to analyzer 検討事項to be considered
実験器具の材質(ガラス or フッ素樹脂、ポリエチレン)
Material of laboratory equipment (glass or fluororesin, polyethylene)
ガラスの利点:疎水性粒子(煤粒子など)の吸着が少ない
Advantage of glass: Less adsorption of hydrophobic particles (such as soot particles)
弱点:ナトリウムイオンの溶出
Weakness: Elution of sodium ions
フッ素樹脂の利点:不純物の溶出がない
Advantages of fluororesin: No elution of impurities
弱点:疎水性粒子の吸着あり
Weak point: Adsorption of hydrophobic particles
ポリエチレンの利点:不純物の溶出が少ない、安価
Advantages of polyethylene: low elution of impurities, low cost
弱点:疎水性粒子の吸着あり
Weak point: Adsorption of hydrophobic particles
試料水の保存(気密方法、保存温度)
Storage of sample water (airtight method, storage temperature)
外部からの汚染を防ぐ、バクテリアの繁殖を防ぐ
Prevent external contamination, prevent bacterial growth