Explanation of entropy ①
Two beakers containing 100 g of water. One is at 0°C, just below the freezing point (Figure A below), and the other is at a hot 90°C (Figure B below). We poured 20 g of boiling water at 100°C, just above the boiling point, into these beakers. For (A), 120 g resulted in about 16°C water, and for (B), 120 g resulted in about 92°C hot water.
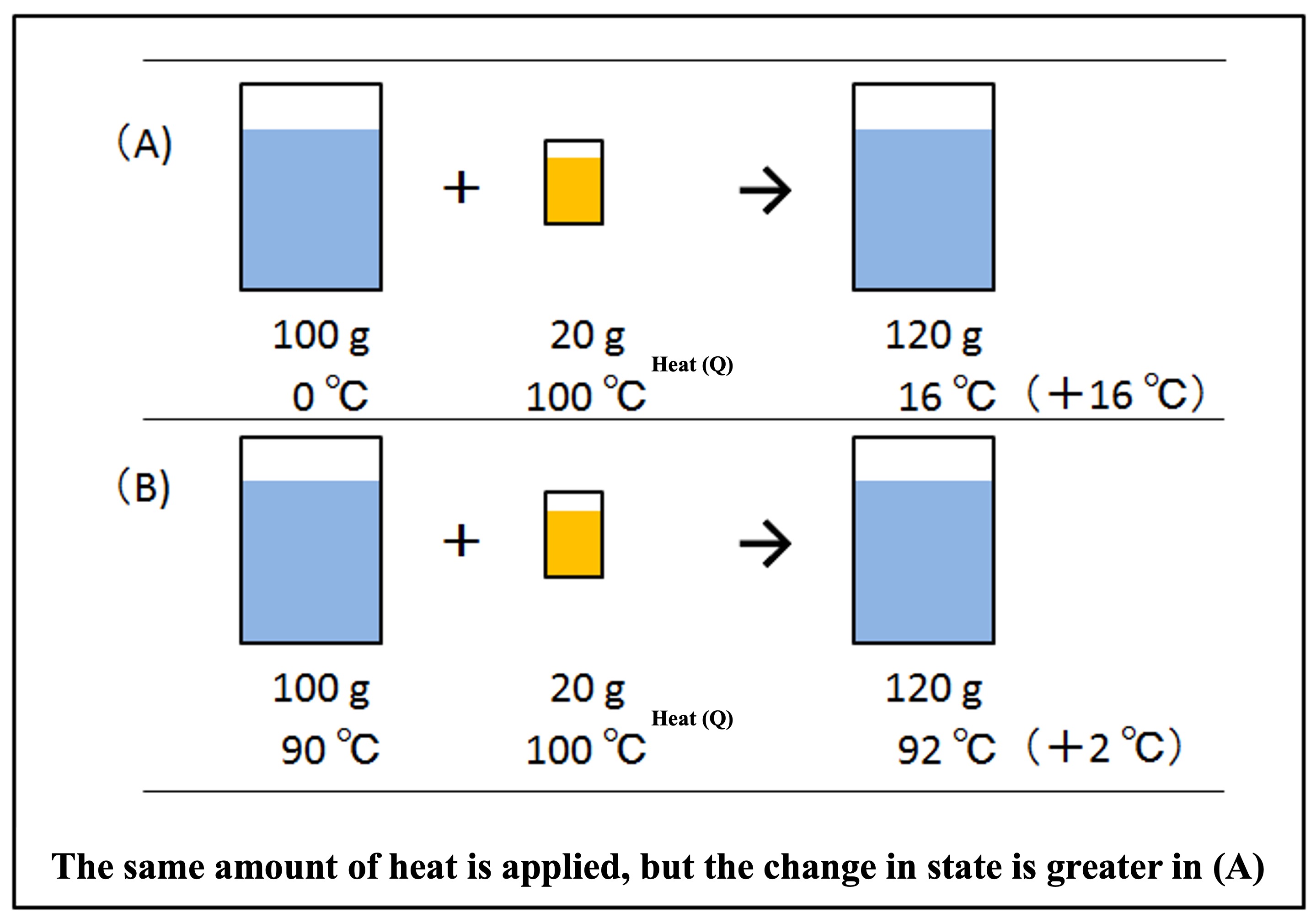
The same amount of heat was added, but (A) rose +16°C, while (B) rose only +2°C. The change in state is greater for (A). To compare the change in state between (A) and (B), we would need some scale. The difference between the two is the original temperature. The lower the original temperature, the greater the change of state.
The amount of heat added (⊿Q: joule) is then divided by the original temperature (T: Kelvin) to define the amount of change in state (⊿S).
This S is called entropy, and ⊿S is called entropy change
(【entropy change ⊿S】 x 【temperature T】 equals the amount of heat (⊿Q) added to the system, and 【entropy S】 x 【temperature T】 is the binding energy).
I don't understand the definition of entropy. Textbooks explain that "entropy is the degree of clutter," which makes it even more confusing.
I will give you some examples so you have an idea of entropy.