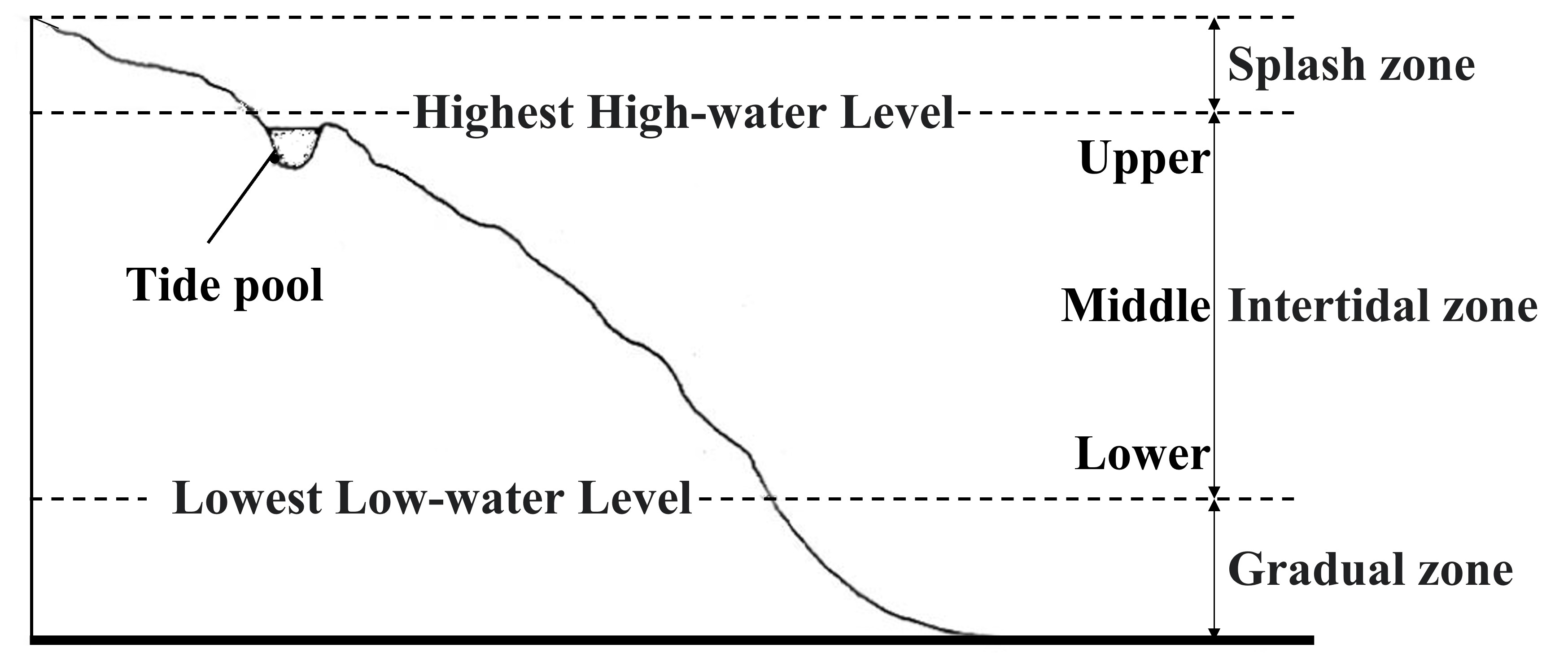
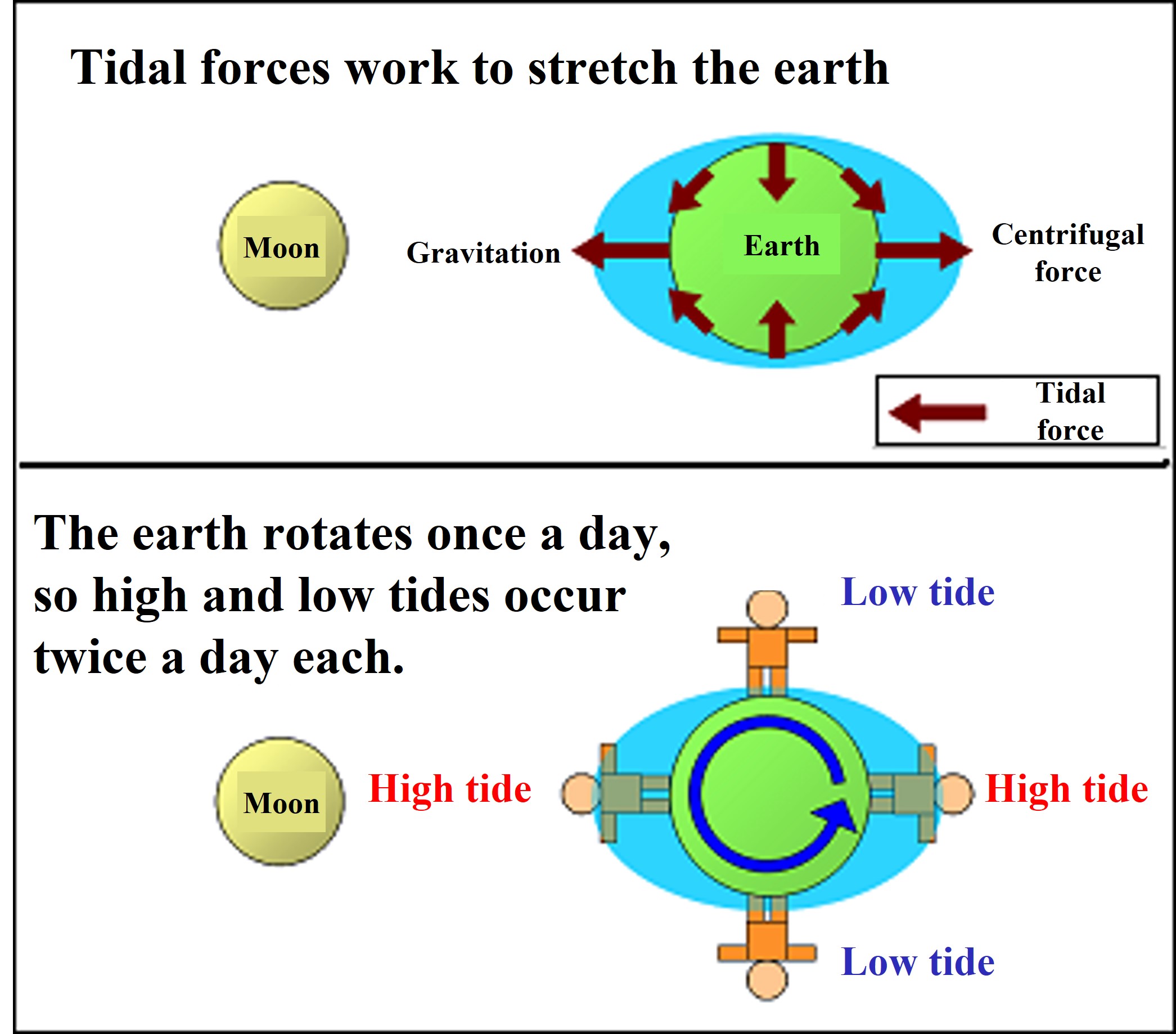
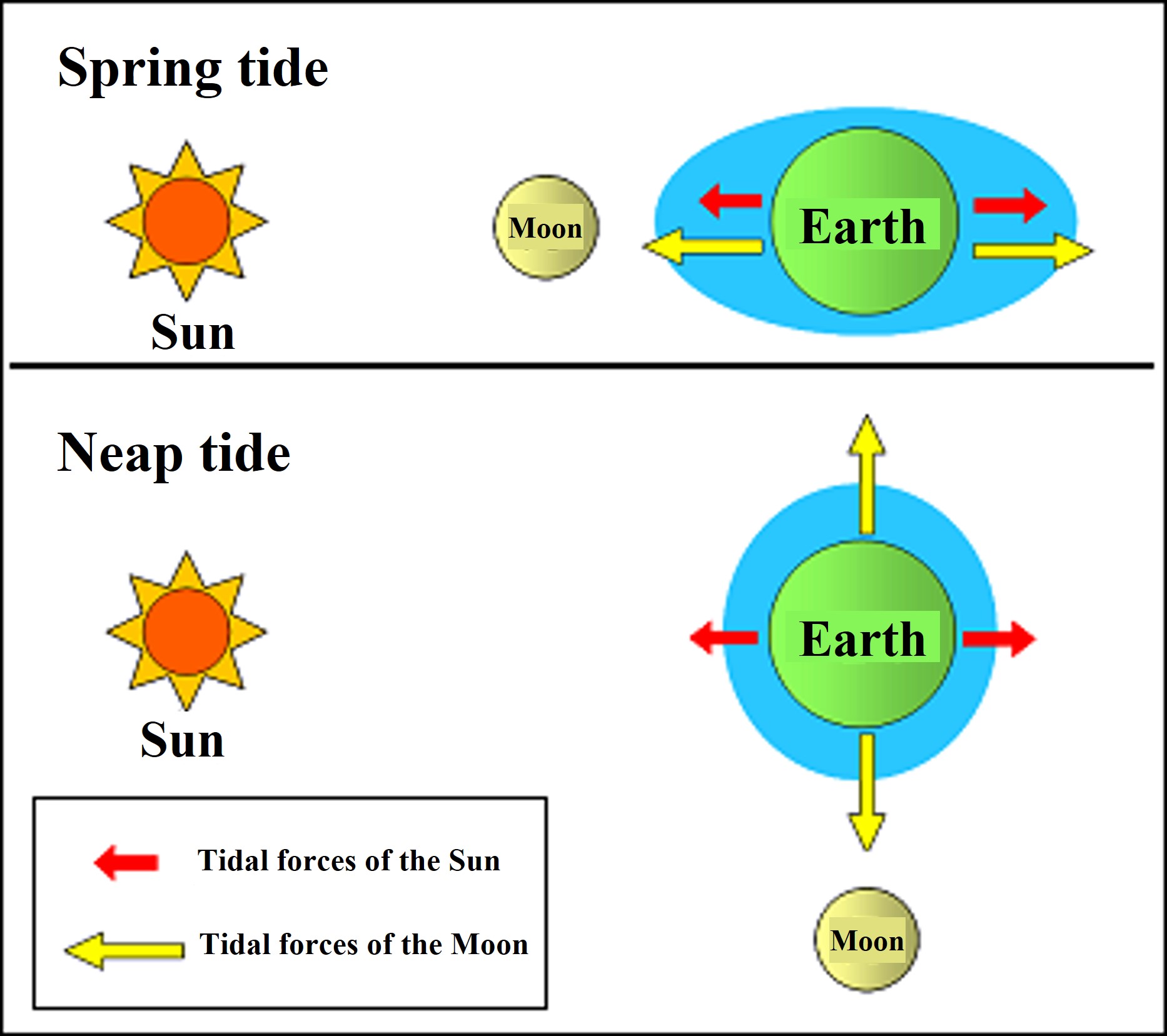
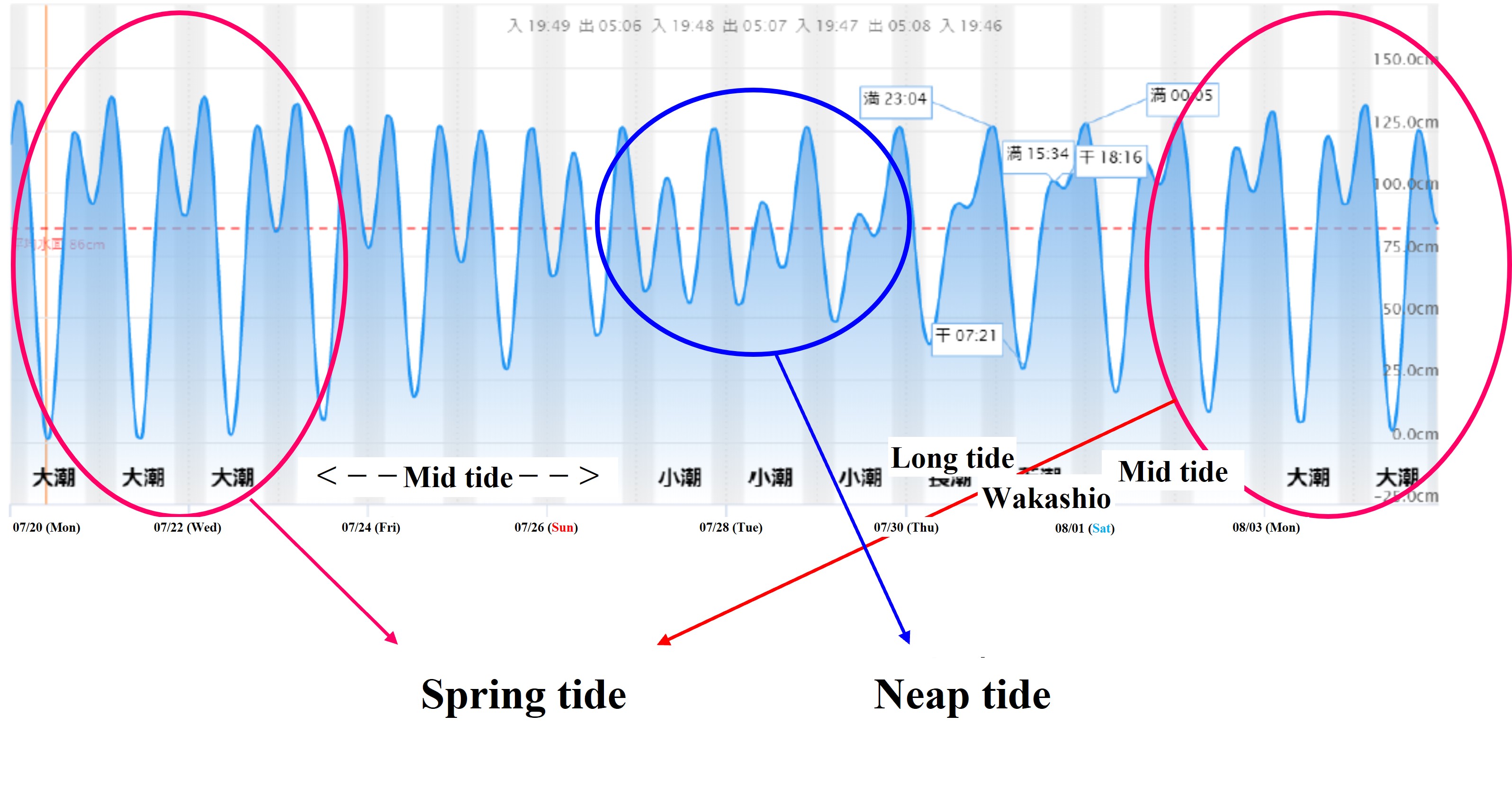
In the rocky intertidal zone, sessile organisms such as seaweed exhibit a zonal distribution with different habitat heights depending on the species. In this practice, the belt transect method is used to investigate its vertical distribution.
Tools:
Rope, quadrat (20cm x 20cm), angle scale, drawing board, underwater notebook, graph paper, pencil, folding scale, silicon tube, plastic bag, box glasses
Method:
(1) A survey line is set by laying a rope at a predetermined survey location (where a zonal distribution can be seen, including from the top of the vertical distribution to the lower part of the intertidal zone).
(2) Place the quadrat along the line, apply the slant rule parallel to the line and record the angle.
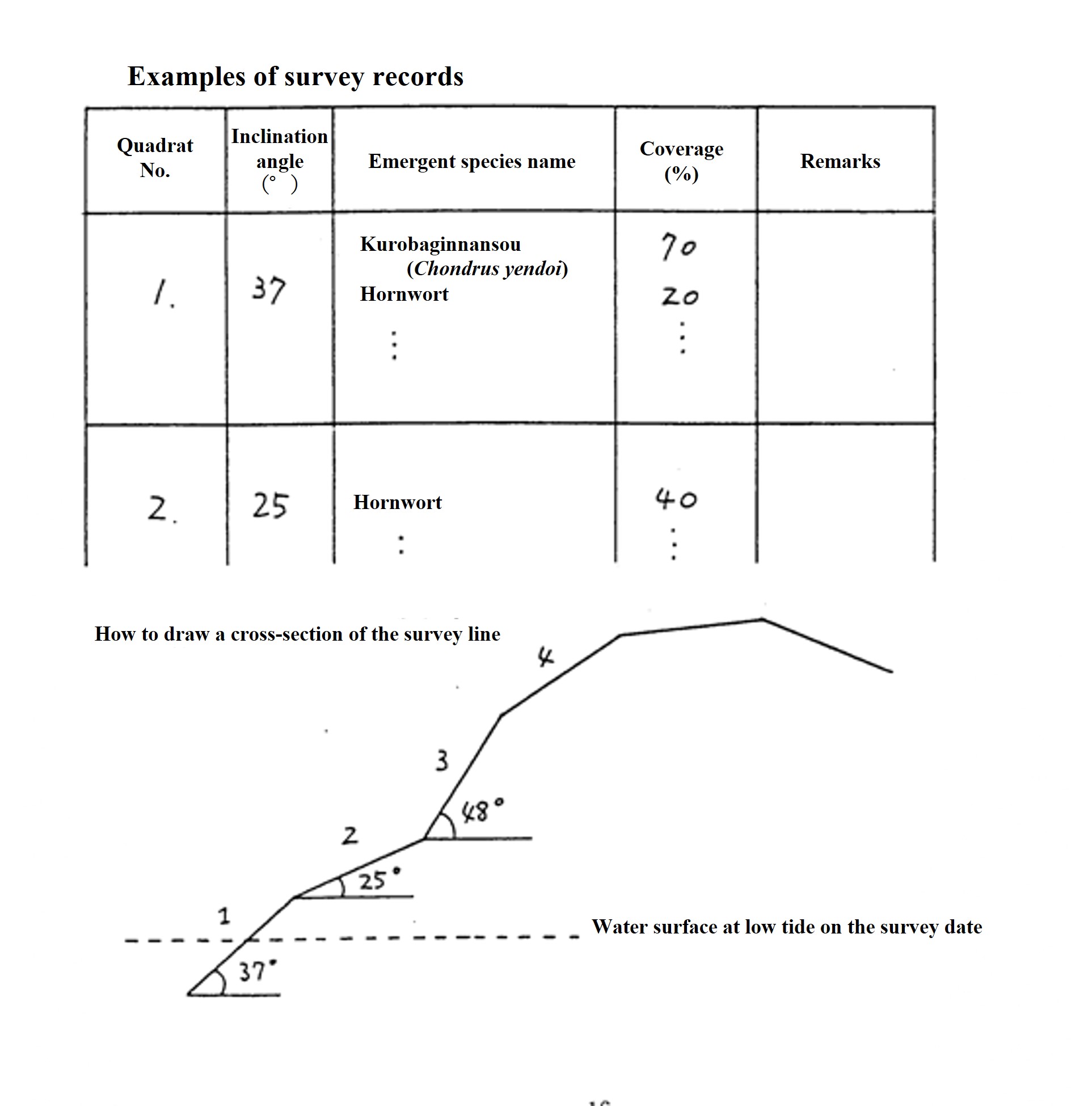
(3) Record the types and coverage of creatures within the quadrat. In addition to algae, sessile animals and creeping animals with a narrow range of movement are also recorded. Coverage is the percentage of the area covered by the organism within the quadrat. The bare surface percentage is also measured and recorded. If it overlaps with other creatures, the total coverage of the species that appeared there may exceed 100%.
Give a value every 10% on the spot. If it is less than 5%, it will be +. Coverage may later be indicated in six ranks as follows:
+(+); 1(5-20%); 2(20-40%); 3(40-60%); 4(60-80%); 5(80-100%)。
If it is difficult to identify the species, bring back the specimen and examine it, or classify it as "Sargassum juvenile" or "Filamentous microalgae". Decide in advance how to classify. Write the quadrat number on the plastic bag and put the creature to bring back there.
It is useful for the scribe to record an approximate cross-sectional profile of the entire survey site for later reconstruction of the profile. It is also a good idea to record the position of the sea surface at the time of the lowest tide in the survey site profile.
(4) Place the quadrat at an adjacent location along the line and make a similar score. This is repeated until the end of the survey line is reached.
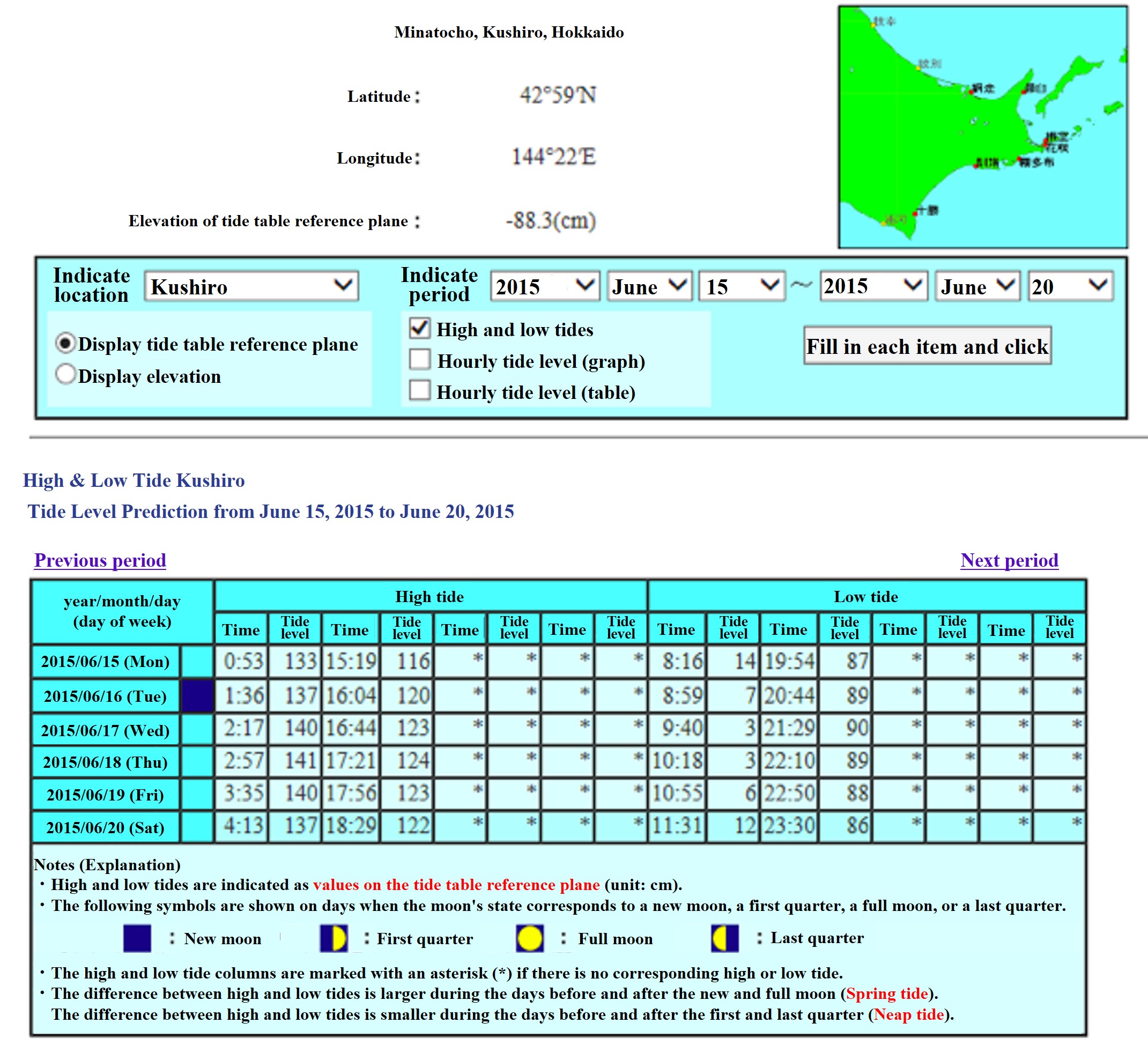
(5) Check the time of low tide and tide level on the day of the survey, and record the actual sea level at that time on the line during the survey.