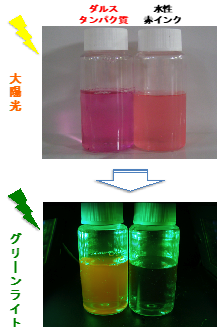
When water is added to a dried dulse
sample, the red component is easily extracted. The color of the extract is
bright red in sunlight and fluoresces strongly when illuminated by green light.
These characteristics are attributed to “phycobiliprotein”, the major protein
in the dulse phloem. In red algae, phycobiliprotein acts as an auxiliary
pigment for photosynthesis, efficiently absorbing light at wavelengths that
chlorophyll cannot.
ダルスタンパク質:dulse protein
水性赤インク: aqueous red ink
太陽光:sunlight
グリーンライト: green light
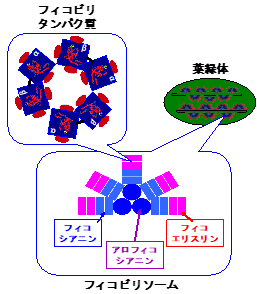
In general, phycobiliproteins of red algae
are mainly composed of two types of subunits, α- and β-chains, which form
circular doughnut-like assemblies consisting of three each of them. These
doughnut-like structures are then further assembled to form a large aggregate
called a phycobilisome. Phycobilisomes are arranged in large numbers on the
surface of the chloroplast thylakoid membrane. The major phycobiliproteins of
red algae are phycoerythrin (red), phycocyanin (blue), and allophycocyanin
(purple). Their coloration is determined by the type of the pigment (phycoerythrobilin,
phycocyanobilin, or phycourobilin) that bound apoprotein of α- and β-chains and number.
Protein extracts prepared from dulse were
subjected to spectral analysis, which revealed that the main component of
phycobiliproteins from dulse is red phycoerythrin, followed by phycocyanin and
allophycocyanin. Therefore, dulse phycoerythrin was purified and crystals were
prepared, and its three-dimensional structure was determined by X-ray
crystallography. As a result, dulse phycoerythrin had the same
three-dimensional structural characteristics as those of other red algae. In
addition, to elucidate the genetic structure of phycobiliproteins from dulse,
chloroplast DNA encoding the genes of phycobiliproteins was analyzed by a
next-generation sequencer. As a result, the gene structures and primary
structures of three phycobiliproteins (phycoerythrin, phycocyanin, and
allophycocyanin) were clarified.
フィコビリタンパク質:phycobiliproteins
葉緑体:chloroplast
フィコシアニン:phycocyanin
アロフィコシアニン:allophycocyanin
フィコエリスリン:phycoerythrin
フィコビリソーム:phycobilisome