Saturation Depth of Calcium Carbonate Particles in the Ocean
Section outline
-
-
Here, the conditional equation for the dissolution of calcium carbonate particles in seawater is written out.
CaCO3 (s) ⇆ Ca2+ + CO32- ;Solubility equilibrium constant Ksp
Ksp = 【Ca2+】×【CO32-】
The supersaturated state is, 【Ca2+】×【CO32-】/ Ksp > 1
The saturated (equilibrium) state is, 【Ca2+】×【CO32-】/ Ksp = 1
Undersaturated state is, 【Ca2+】×【CO32-】/ Ksp < 1.
-
The figure below shows the depth at which calcite (top) and aragonite (bottom) among calcium carbonate particles become saturated (【Ca2+】×【CO32-】/ Ksp = 1). Shallower than this depth, calcium carbonate particles will not dissolve because they are undersaturated. In the North Atlantic, calcite is undersaturated (dissolves) at depths below 4500 m, indicating that it is not dissolved in deep water down to about 4000 m depth. In the North Pacific, calcite is undersaturated (dissolved) at depths below 500 m.
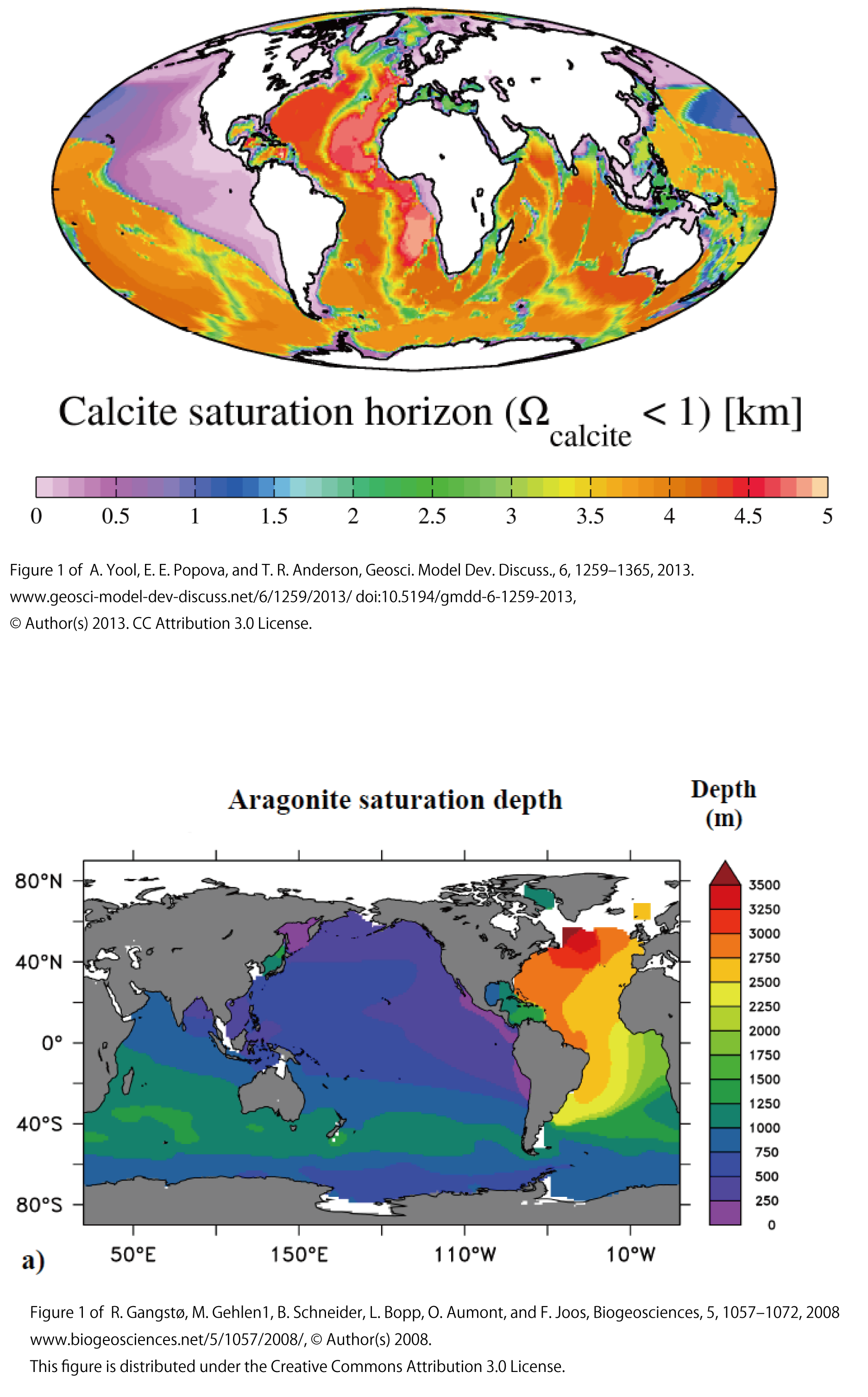
-

