Alkalinity and Dissolution of Calcium Carbonate Particles in the Ocean
섹션 개요
-
-
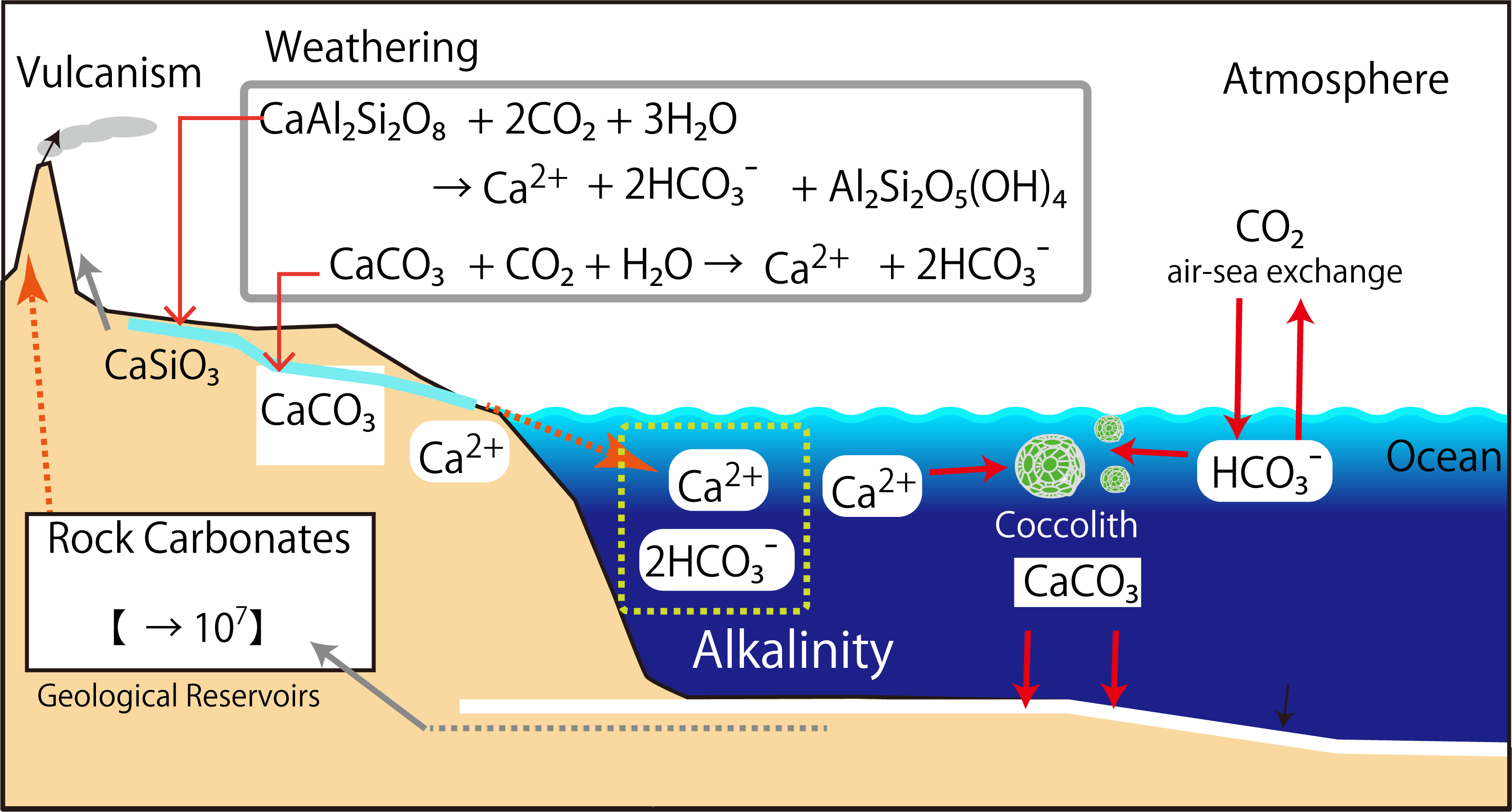
The formation and dissolution of calcium carbonate particles is a major determinant of the alkalinity in the ocean. The conditions under which calcium carbonate particles dissolve in seawater are described below. Calcium carbonate particles in surface seawater do not dissolve permanently. This is because surface seawater is supersaturated with calcium carbonate. In deep seawater, under some conditions, it is undersaturated for calcium carbonate and the particles will dissolve.
Why was this found to be the case? It is because it is clear that the compositional distribution of marine sediments differs greatly between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Compositional distribution of marine sediments
Introduction to Oceanography by Paul Webb, figure 12.6.1 used under a CC-BY 4.0 international license.
Download this book for free at http://rwu.pressbooks.pub/webboceanography
The figure 12.6.1 was referred from Steven Earle, “Physical Geology” open access text book) -
Dissolution of calcium carbonate particles proceeds when the concentration of carbonate ions in seawater decreases (pH drops) and pressure increases. The figure below illustrates how biogenic calcium carbonate particles produced in the ocean surface layer settle out and are deposited on the seafloor. It is divided into three layers.
The depth at which carbonate particles are deposited and dissolved
-