Composition of Organic Matter
Section outline
-
-
Organisms (organic matter) are composed of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. The average composition ratio of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in marine organisms is said to be C:N:P = 106:16:1 (Redfield ratio). In ocean chemistry, it is of interest to note how the composition ratios of organic matter and seawater change. This is because this ratio often reflects the state of ocean ecology.
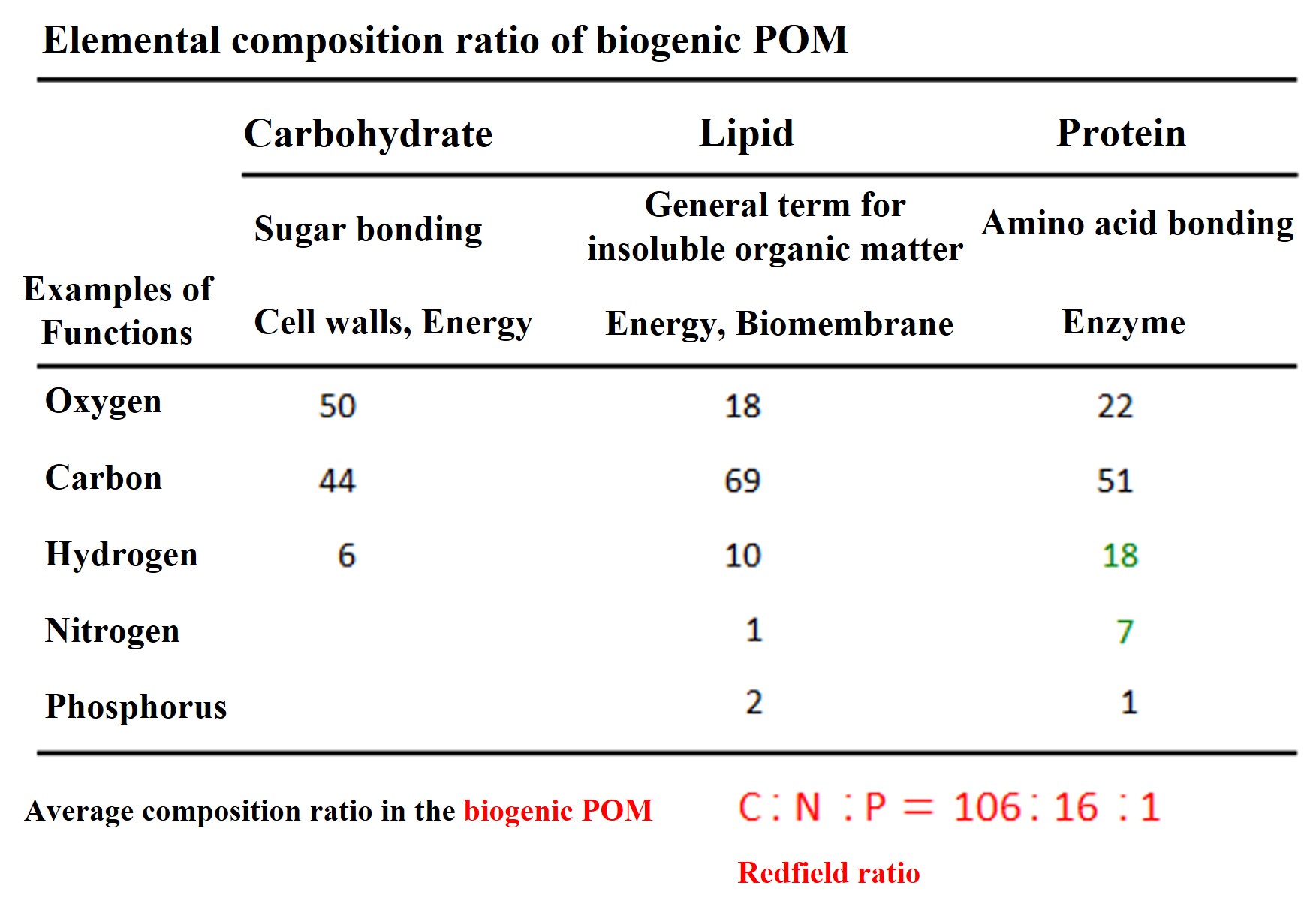
-
When an organism dies, do the components of its organic matter decompose uniformly? Among the components of living organisms, "cell walls" have a tough structure and will not decompose easily. Enzymes, on the other hand, are highly reactive and will decompose quickly if immersed in seawater. The average composition of particulate organic matter (POM) and dissolved organic matter (DOM) varies depending on the organic matter composition and degradability.
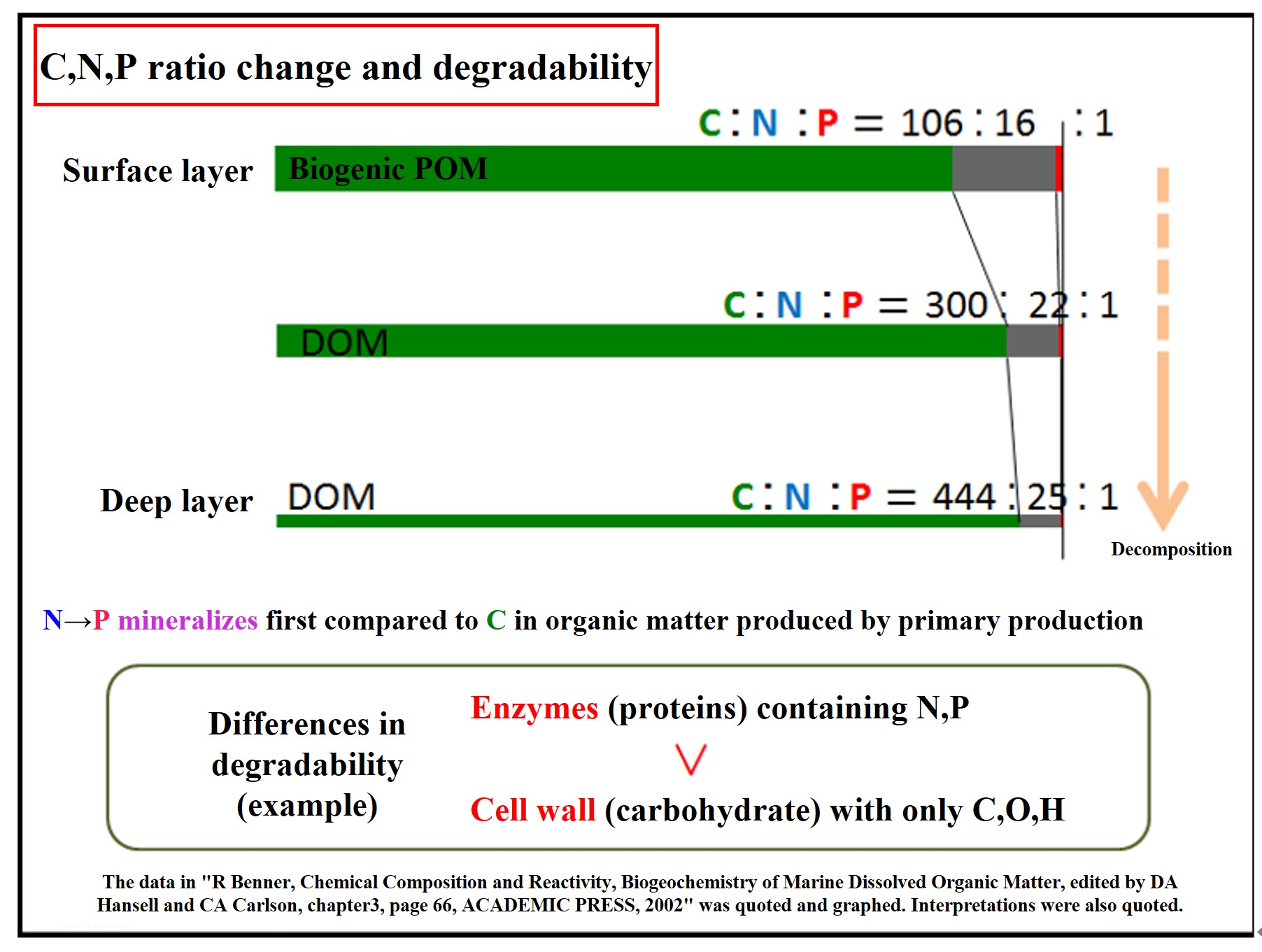
-
It summarizes the history of research on the Redfield ratio, its geochemical background, and its relationship to nutrient uptake by phytoplankton. It mentions the need to revise the Redfield ratio because globally the N/P ratio of deep water is 15. It also states that under nutrient-rich seawater conditions, phytoplankton in the log growth phase takes up nutrients at an N/P ratio of 8.2. Chapter 6, "6. The Original Meaning of the Redfield Ratio," is something of a challenge.
This is a very informative review paper and I encourage everyone to read it. Please take a moment to read it, as you will be using your knowledge of this review paper for your report assignment in the "Nutrients" chapter of this class.
-

