Chromatography is a separation method that utilizes the adsorption and desorption properties of chemical components.Chromatography began when petroleum ether was passed through a column filled with calcium carbonate and separated as adsorption bands of different colors.For this reason, it came to be called Chromatography, which means "record of colors", from the Greek words Chroma (color) and Graphos (record).
(Quoted from Nishikawa Keisoku HP information)
A chromatograph is a chromatography device.
A chromatogram is a graph of time-series changes in signal intensity separated and measured by a chromatograph (device) (explained later).
Ion chromatography is a method for separating and analyzing ionic components in water.
Gas chromatography is a method for separating and analyzing components in the gas phase.
Below is an image of separation analysis using ion chromatography as an example.Water contains multiple ingredients. Multiple types are expressed with different colors.Once mixed, you won't know what ingredients are in them and how much.Pass the mixed solution through an ion exchange resin column. Taking advantage of the fact that each component takes a different amount of time to pass through the column, each component (color) is separated when it comes out of the column. The components are separated along the flow of the liquid, and a detector is placed downstream. By monitoring the signal strength, the concentration of each component can be determined.
There are various types of detectors. For ion chromatography, the simplest measure is electrical conductivity. If concentrated ionic components flow, the electrical conductivity will increase. There is also a fluorescence detector. Components that absorb light and emit fluorescence can be detected with high sensitivity.
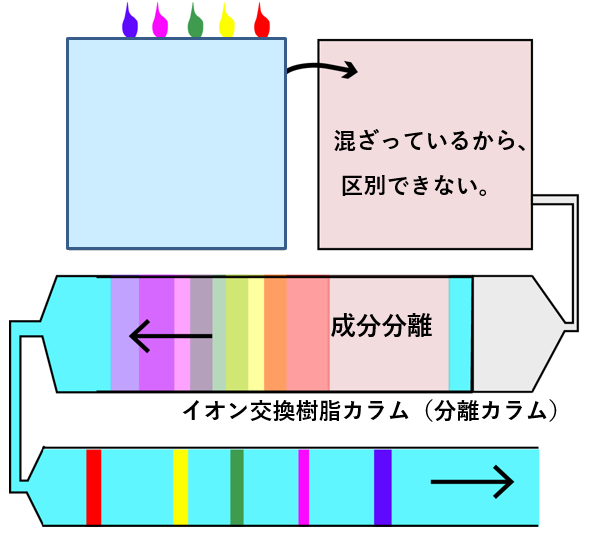
混ざっているから区別できないI can't tell them apart because they're mixed together. 成分分離component separation イオン交換樹脂カラムIon exchange resin column 分離カラムseparation column