Using the entropy change equation above, let's actually calculate the amount of entropy change.
First, for one mole of ideal gas, the entropy change when the temperature is kept constant (Ln(T1/T0) = 0) and the volume is increased tenfold is ⊿S = R・Ln(10) = 19.3 (J/K). When the volume is restored, ⊿S = -19.3 (J/K) as well.
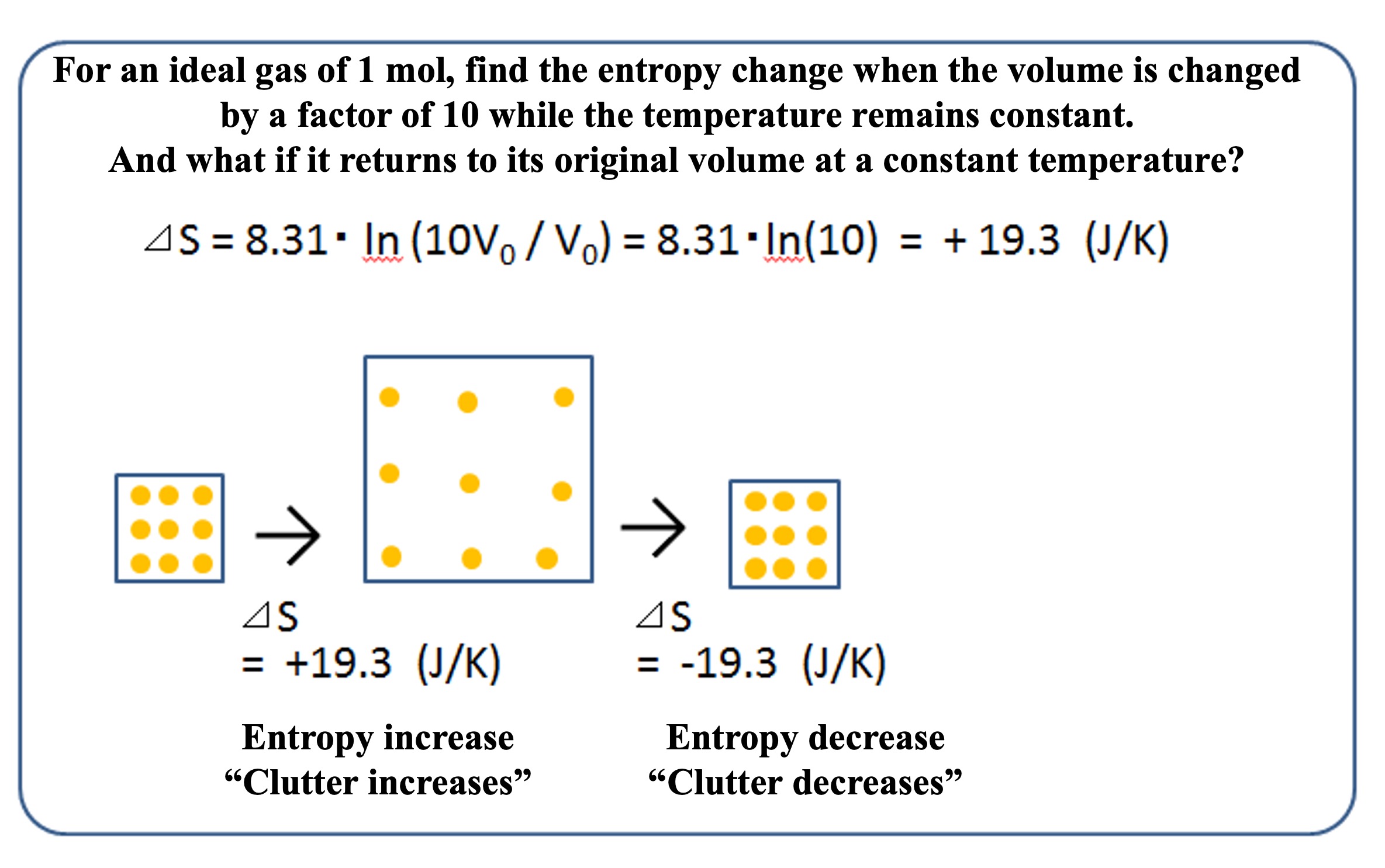
Earlier, I mentioned that entropy always increases, and this is only true for adiabatic systems. It is possible to decrease the entropy of a substance, and in doing so, heat must be transferred to the outside world.
Examples of calculations of entropy change are still to come.