What are MAAs?
セクションアウトライン
-
MAAs are water-soluble low molecular weight compounds synthesized by the shikimic acid and pentose phosphate pathways and are secondary metabolites with cyclohexanone and cyclohexceimine as their basic backbone (Figure 2). Sunlight contains ultraviolet rays that are harmful to living organisms. Ultraviolet radiation is classified into UVA (315-400 nm), UVB (280-315 nm), and UVC (100-280 nm) according to its wavelength range. UVA and UVB reach the earth's surface and cause structural changes in proteins and nucleic acids, while MAAs have absorption maxima between 310 and 360 nm and emit light energy as heat.
Shikimic acid pathway: A pathway by which microorganisms and plants biosynthesize aromatic amino acids (tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophan).
Pentose phosphate pathway: A pathway in the glycolytic system mainly involved in the biosynthesis of five-carbon sugars (ribose and deoxyribose).
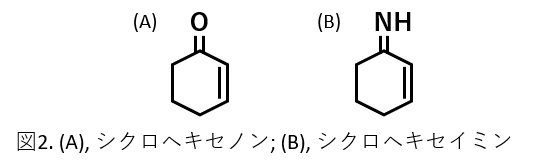
Figure 2. (A), Cyclohexenone; (B), Cyclohexaymin

