When
rabbits are injected with purified fish proteins, the rabbits recognize them as
foreign substances and produce antibodies. This antibody binds to the injected
protein but not to the others. A chromogenic/luminescent substrate is attached
to the antibody, and the amount of binding is detected and measured as color or
luminosity.
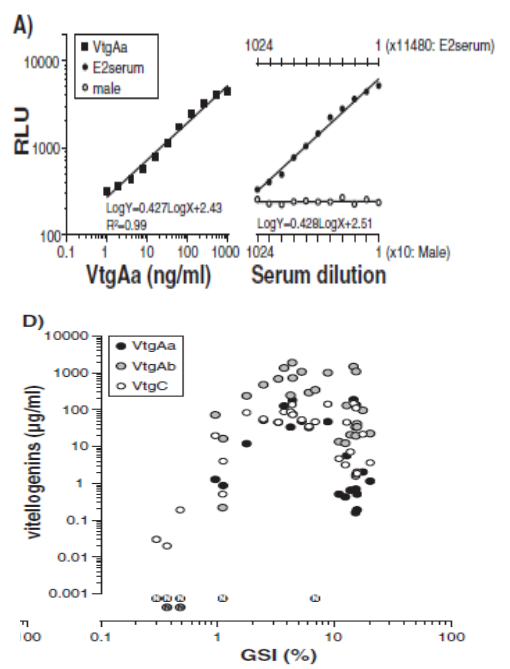
Immunochemical
assay
systems for yolk protein precursors:
The figure on the left shows the
standard curve (luminance on the vertical axis and VtgAa
concentration on the horizontal axis) and the serum dilution series (Male serum
○, serum containing VtgAa
●) of the chemoluminescence
immunoassay system for the yolk protein precursor (synonymous with VtgAa
= VgA)
of mullet (Mugil
cephalus).
The
higher the VtgAa, the higher the luminosity value, and antibodies
don′t
react with other contaminating seroproteins (male serum).
Example
of measurement of yolk protein precursors:
The figure on the left shows the
immunochemical measurement of three types of Vtg
using mullet serum at various stages of sexual maturity. The vertical axis is Vtg
concentration, and the horizontal axis is gonad weight per body weight (gonad
body index: GSI). Early
in sexual maturation, Vtg
levels are low. When GSI exceeds 10% and Vtg
levels tend to decrease as spawning approaches. Continuous
monitoring of Vtg as a blood marker for maturity and egg maturation can predict
the timing of spawning and hormone
administrations.