Isoprene
Section outline
-
-
Isoprene (
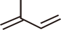 ) is a hydrocarbon with two double bonds, and its chemical formula is C5H8
) is a hydrocarbon with two double bonds, and its chemical formula is C5H8Plants synthesize organic matter, such as carotene, using isoprene units (
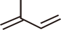 ). Because
isoprene is highly volatile, it has been shown to be released outside the plant
during photosynthesis. Atmospheric isoprene derived from plants accounts for a large portion of natural organic gas. Isoprene is also released from
marine plants, and it is thought to change the oxidation capacity of the marine
atmosphere. In the dark, where photosynthesis is not possible, plants decompose
carotene to obtain energy. Isoprene is likely to be released at this time as
well. In this
research,
we investigate
the production rate of isoprene by oceanic phytoplankton communities, as well
as the production in the dark.
). Because
isoprene is highly volatile, it has been shown to be released outside the plant
during photosynthesis. Atmospheric isoprene derived from plants accounts for a large portion of natural organic gas. Isoprene is also released from
marine plants, and it is thought to change the oxidation capacity of the marine
atmosphere. In the dark, where photosynthesis is not possible, plants decompose
carotene to obtain energy. Isoprene is likely to be released at this time as
well. In this
research,
we investigate
the production rate of isoprene by oceanic phytoplankton communities, as well
as the production in the dark.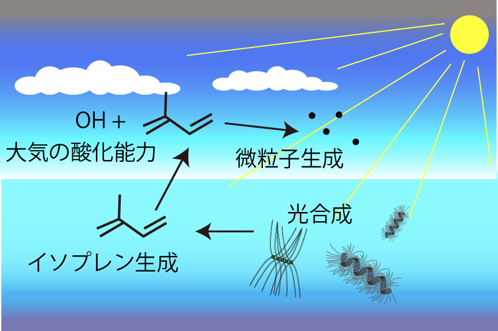
-

